Environmental and Health Effects of Ventilation in Subway Stations: A Literature Review
- PMID: 32046319
- PMCID: PMC7037944
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17031084
Environmental and Health Effects of Ventilation in Subway Stations: A Literature Review
Abstract
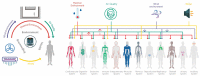
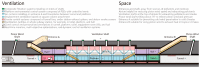
Environmental health in subway stations, a typical type of urban underground space, is becoming increasingly important. Ventilation is the principal measure for optimizing the complex physical environment in a subway station. This paper narratively reviews the environmental and health effects of subway ventilation and discusses the relevant engineering, environmental, and medical aspects in combination. Ventilation exerts a notable dual effect on environmental health in a subway station. On the one hand, ventilation controls temperature, humidity, and indoor air quality to ensure human comfort and health. On the other hand, ventilation also carries the potential risks of spreading air pollutants or fire smoke through the complex wind environment as well as produces continuous noise. Assessment and management of health risks associated with subway ventilation is essential to attain a healthy subway environment. This, however, requires exposure, threshold data, and thereby necessitates more research into long-term effects, and toxicity as well as epidemiological studies. Additionally, more research is needed to further examine the design and maintenance of ventilation systems. An understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms and aerodynamic characteristics of various pollutants can help formulate ventilation strategies to reduce pollutant concentrations. Moreover, current comprehensive underground space development affords a possibility for creating flexible spaces that optimize ventilation efficiency, acoustic comfort, and space perception.
Keywords: environmental effect; health effect; mitigation measure; review; subway; ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Loo B.P.Y., Chen C., Chan E.T.H. Rail-based transit-oriented development: Lessons from New York City and Hong Kong. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010;97:202–212. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.06.002. - DOI
-
- Papa E., Bertolini L. Accessibility and Transit-Oriented Development in European metropolitan areas. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015;47:70–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2015.07.003. - DOI
-
- Sung H., Oh J.-T. Transit-oriented development in a high-density city: Identifying its association with transit ridership in Seoul, Korea. Cities. 2011;28:70–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2010.09.004. - DOI
-
- Yang J., Chen J., Le X., Zhang Q. Density-oriented versus development-oriented transit investment: Decoding metro station location selection in Shenzhen. Transp. Policy. 2016;51:93–102. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2016.04.004. - DOI
-
- Reche C., Moreno T., Martins V., Minguillón M.C., Jones T., de Miguel E., Capdevila M., Centelles S., Querol X. Factors controlling particle number concentration and size at metro stations. Atmos. Environ. 2017;156:169–181. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.03.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical