Luteinizing Hormone Action in Human Oocyte Maturation and Quality: Signaling Pathways, Regulation, and Clinical Impact
- PMID: 32046451
- PMCID: PMC7190682
- DOI: 10.1007/s43032-019-00137-x
Luteinizing Hormone Action in Human Oocyte Maturation and Quality: Signaling Pathways, Regulation, and Clinical Impact
Abstract
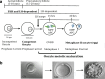
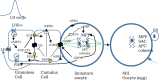
The ovarian follicle luteinizing hormone (LH) signaling molecules that regulate oocyte meiotic maturation have recently been identified. The LH signal reduces preovulatory follicle cyclic nucleotide levels which releases oocytes from the first meiotic arrest. In the ovarian follicle, the LH signal reduces cyclic nucleotide levels via the CNP/NPR2 system, the EGF/EGF receptor network, and follicle/oocyte gap junctions. In the oocyte, reduced cyclic nucleotide levels activate the maturation promoting factor (MPF). The activated MPF induces chromosome segregation and completion of the first and second meiotic divisions. The purpose of this paper is to present an overview of the current understanding of human LH signaling regulation of oocyte meiotic maturation by identifying and integrating the human studies on this topic. We found 89 human studies in the literature that identified 24 LH follicle/oocyte signaling proteins. These studies show that human oocyte meiotic maturation is regulated by the same proteins that regulate animal oocyte meiotic maturation. We also found that these LH signaling pathway molecules regulate human oocyte quality and subsequent embryo quality. Remarkably, in vitro maturation (IVM) prematuration culture (PMC) protocols that manipulate the LH signaling pathway improve human oocyte quality of cultured human oocytes. This knowledge has improved clinical human IVM efficiency which may become a routine alternative ART for some infertile patients.
Keywords: LH follicle signaling; Oocyte meiotic maturation; Oocyte quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Greenwald GaR SK. Follicular development and its control. In: Knobil E, editor. The physiology of reproduction. 2. New York: Raven Press; 1994. pp. 629–724.
-
- Pincus G. The eggs of mammals. Experimental Biology Monographs. New York, NY; The Macmillian Company; 1936.
-
- Sanchez F, Smitz J. Molecular control of oogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822;2012:1896–1912. - PubMed
-
- Coticchio G, Dal Canto M, Mignini Renzini M, Guglielmo MC, Brambillasca F, Turchi D, Novara PV, Fadini R. Oocyte maturation: gamete-somatic cells interactions, meiotic resumption, cytoskeletal dynamics and cytoplasmic reorganization. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21:427–454. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

