Association of the Promoter Haplotype of IFN-γ-Inducible Protein 16 Gene with Schizophrenia in a Korean Population
- PMID: 32046472
- PMCID: PMC7047005
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2019.0175
Association of the Promoter Haplotype of IFN-γ-Inducible Protein 16 Gene with Schizophrenia in a Korean Population
Abstract
Objective: Viral infections play an important role in the development of schizophrenia, inducing the faulty immunological responses and aberrant inflammation. IFN-γ-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) is an immunological DNA sensor against viral infections, triggering the inflammatory responses. In this study, we investigated an association between putative promoter single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and haplotypes of IFI16 and schizophrenia.
Methods: A total of 280 schizophrenia patients and 427 control subjects were recruited in this study. We genotyped three promoter SNPs (rs1465175, rs3754464, rs1417806) using direct sequencing. Associations of SNPs and haplotypes of IFI16 with schizophrenia were analyzed. The promoter activities on the haplotypes of IFI16 were measured.
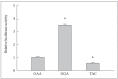
Results: The T allele of rs1465175 and the C allele of rs1417806 were protectively associated with schizophrenia (p=0.021 on rs1465175; p=0.016 on rs1417806), whereas the G allele of rs3754464 was associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia (p=0.019). In haplotype analysis, a significant association between the GGA haplotype and schizophrenia was shown (p=0.013). Moreover, we found that the GGA haplotype elevated the promoter activity compared to the GAA haplotype, whereas the TAC haplotype reduced that.
Conclusion: The promoter SNPs and haplotypes of IFI16 may contribute to the susceptibility of schizophrenia, affecting the promoter activity of IFI16.
Keywords: IFN-γ-inducible protein 16; Promoter activity; Schizophrenia; Single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cutting Edge: Genetic Association between IFI16 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Resistance to Genital Herpes Correlates with IFI16 Expression Levels and HSV-2-Induced IFN-β Expression.J Immunol. 2017 Oct 15;199(8):2613-2617. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700385. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28893956
-
Genetic associations of Nrf2-encoding NFE2L2 variants with Parkinson's disease - a multicenter study.BMC Med Genet. 2014 Dec 12;15:131. doi: 10.1186/s12881-014-0131-4. BMC Med Genet. 2014. PMID: 25496089 Free PMC article.
-
Variants of the IFI16 gene affecting the levels of expression of mRNA are associated with susceptibility to Behçet disease.J Rheumatol. 2015 Apr;42(4):695-701. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.140949. Epub 2015 Feb 1. J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25641891
-
Association analysis of the RGS4 gene in Han Chinese and Scottish populations with schizophrenia.Genes Brain Behav. 2005 Oct;4(7):444-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2005.00167.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2005. PMID: 16176390
-
The role of IFI16 in regulating PANoptosis and implication in heart diseases.Cell Death Discov. 2024 May 1;10(1):204. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01978-5. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38693141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown AS, Begg MD, Gravenstein S, Schaefer CA, Wyatt RJ, Bresnahan M, et al. Serologic evidence of prenatal influenza in the etiology of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:774–780. - PubMed
-
- Bechter K. Updating the mild encephalitis hypothesis of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;42:71–91. - PubMed
-
- Yolken RH, Torrey EF, Lieberman JA, Yang S, Dickerson FB. Serological evidence of exposure to Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 is associated with cognitive deficits in the CATIE schizophrenia sample. Schizophr Res. 2011;128:61–65. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

