Comparative study of hyperpolarization-activated currents in pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes isolated from rat, guinea pig, and rabbit
- PMID: 32046630
- PMCID: PMC7012960
- DOI: 10.1186/s12576-020-00736-3
Comparative study of hyperpolarization-activated currents in pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes isolated from rat, guinea pig, and rabbit
Abstract
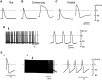
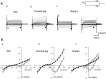
Pulmonary vein (PV) cardiomyocytes have the potential to generate spontaneous activity, in contrast to working myocytes of atria. Different electrophysiological properties underlie the potential automaticity of PV cardiomyocytes, one being the hyperpolarization-activated inward current (Ih), which facilitates the slow diastolic depolarization. In the present study, we examined pharmacological characteristics of the Ih of PV cardiomyocytes in rat, guinea pig and rabbit. The results showed that guinea pig and rat PV cardiomyocytes possessed sizeable amplitudes of the Ih, and the Ih of guinea pig was suppressed by Cs+, a blocker of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current. However, the Ih of rat was not suppressed by Cs+, but by Cd2+, a blocker of the Cl- current. The current density of the Ih of rabbit PV cardiomyocytes was significantly smaller than those of other species. This suggests that the ion channels that carry the Ih of PV cardiomyocytes differ among the animal species.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Automaticity; Hyperpolarization-activated Cl− current; Hyperpolarization-activated cation current; Pulmonary vein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pathological impact of hyperpolarization-activated chloride current peculiar to rat pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jan;66:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24239603
-
Molecular identification of HSPA8 as an accessory protein of a hyperpolarization-activated chloride channel from rat pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 1;294(44):16049-16061. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007416. Epub 2019 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31506297 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous expression of potassium currents and pacemaker currents potentially regulates arrhythmogenesis of pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2009 Sep;20(9):1039-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2009.01480.x. Epub 2009 May 15. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19473300
-
Characterization of a hyperpolarization-activated time-dependent potassium current in canine cardiomyocytes from pulmonary vein myocardial sleeves and left atrium.J Physiol. 2004 Jun 1;557(Pt 2):583-97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.061119. Epub 2004 Mar 12. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15020696 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary vein myocardium as a possible pharmacological target for the treatment of atrial fibrillation.J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;126(1):1-7. Epub 2014 Aug 23. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25242082 Review.
Cited by
-
Automatic Activity Arising in Cardiac Muscle Sleeves of the Pulmonary Vein.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 24;12(1):23. doi: 10.3390/biom12010023. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 35053171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automaticity of the Pulmonary Vein Myocardium and the Effect of Class I Antiarrhythmic Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;25(22):12367. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212367. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 modulates pacemaker ion channels differentiation in P19-derived pluripotent cells.J Physiol Sci. 2020 Sep 7;70(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12576-020-00766-x. J Physiol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32895058 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of hyperpolarization-activated cation current on conduction delay and failure of action potentials along axon related to abnormal functions.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Oct;18(5):2433-2453. doi: 10.1007/s11571-024-10103-2. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39555253
-
Comparative Study of Transcriptome in the Hearts Isolated from Mice, Rats, and Humans.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 20;12(6):859. doi: 10.3390/biom12060859. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ye W, Wang J, Song Y, Yu D, Sun C, Liu C, Chen F, Zhang Y, Wang F, Harvey RP, Schrader L, Martin JF, Chen Y. A common Shox2-Nkx2-5 antagonistic mechanism primes the pacemaker cell fate in the pulmonary vein myocardium and sinoatrial node. Development. 2015;142:2521–2532. doi: 10.1242/dev.120220. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

