Next-generation sequencing identified novel Desmoplakin frame-shift variant in patients with Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 32046637
- PMCID: PMC7011609
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-020-01369-5
Next-generation sequencing identified novel Desmoplakin frame-shift variant in patients with Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (AC) is one of the leading causes for sudden cardiac death (SCD). Recent studies have identified mutations in cardiac desmosomes as key players in the pathogenesis of AC. However, the specific etiology in individual families remains largely unknown.
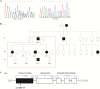
Methods: A 4-generation family presenting with syncope, lethal ventricular arrhythmia and SCD was recruited. Targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) was performed and validated by Sanger sequencing. Plasmids containing the mutation and wild type (WT) were constructed. Real-time PCR, western-blot and immunofluorescence were performed to detect the functional change due to the mutation.
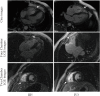
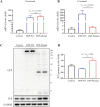
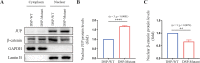
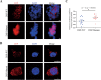
Results: The proband, a 56-year-old female, presented with recurrent palpitations and syncope. An ICD was implanted due to her family history of SCD/ aborted SCD. NGS revealed a novel heterozygous frame-shift variant (c.832delG) in Desmoplakin (DSP) among 5 family members. The variant led to frame-shift and premature termination, producing a truncated protein. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) of the family members carrying the same variant shown myocardium thinning and fatty infiltration in the right ventricular, positive bi-ventricular late gadolinium enhancement and severe RV dysfunction, fulfilling the diagnostic criteria of AC. HEK293T cells transfected with mutant plasmids expressed truncated DSP mRNA and protein, upregulation of nuclear junction plakoglobin (JUP) and downregulation of β-catenin, when compared with WT.
Conclusion: We infer that the novel c.832delG variant in DSP was associated with AC in this family, likely through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; Desmoplakin; Genetic variant; Next generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Marcus FI, McKenna WJ, Sherrill D, Basso C, Bauce B, Bluemke DA, Calkins H, Corrado D, Cox MG, Daubert JP, et al. Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: proposed modification of the task force criteria. Circulation. 2010;121(13):1533–1541. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.840827. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- WKJ-ZJ-1703/Provincial and Ministry Joint Major Projects of National Health Commission of China/International
- 81470384/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81870203/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81670259/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81670304/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

