Body fat percentage and CRP correlates with a composite score of vascular risk markers in healthy, young adults - The Lifestyle, Biomarkers, and Atherosclerosis (LBA) study
- PMID: 32046640
- PMCID: PMC7014751
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-020-01376-6
Body fat percentage and CRP correlates with a composite score of vascular risk markers in healthy, young adults - The Lifestyle, Biomarkers, and Atherosclerosis (LBA) study
Abstract
Background: Identification of early signs of atherosclerosis in young adults have the potential to guide early interventions to prevent later cardiovascular disease. We therefore analyzed measures of vascular structure and function and biomarkers of cardiovascular risk in a sample of young healthy adults.
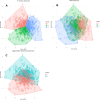
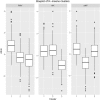
Methods: Pulse-wave velocity (PWV), carotid-intima media thickness (cIMT) and augmentation index (AIX) were measured in 834 healthy non-smokers (ages 18.0-25.9). Emphasis was put on discriminating between individuals having a vascular structure and function associated with a higher or lower risk, and cluster analysis algorithms were employed to assign the subjects into groups based on these vascular measurements. In addition, a vascular status score (VSS) was calculated by summarizing the results according to quintiles of the vascular measurements. The associations between VSS and cardiovascular biomarkers were examined by regression analyses.
Results: The cluster analyses did not yield sufficiently distinct clustering (groups of individuals that could be categorized unequivocally as having either a vascular structure and function associated with a higher or lower CVD risk). VSS proved a better classificatory variable. The associations between VSS and biomarkers of cardiovascular risk were analyzed by univariable and multivariable regressions. Only body fat percentage and C-reactive protein (CRP) were independently associated with VSS.
Conclusions: A VSS calculation, which integrates PWV, cIMT, and AIX measurements is better suited for cardiovascular risk evaluation in young adults than cluster analyses. The independent associations of VSS with body fat percentage and CRP highlight the decisive role of adiposity and systemic inflammation in early atherosclerotic progression and suggests a subordinate role of insulin and lipid metabolism in this age span.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Body fat percentage; CRP; Cardiovascular risk; Cluster analysis; Endothelial dysfunction; Obesity; Young adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Body composition is a strong predictor of local carotid stiffness in Swedish, young adults - the cross sectional Lifestyle, biomarkers, and atherosclerosis study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 Aug 27;19(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1180-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 31455254 Free PMC article.
-
Pulse wave velocity, augmentation index, and carotid intima-media thickness are each associated with different inflammatory protein signatures in young healthy adults: The lifestyle, biomarkers and atherosclerosis study.Atherosclerosis. 2020 Nov;313:150-155. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.09.027. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Atherosclerosis. 2020. PMID: 33059161
-
The role of inflammation in the association between overall and visceral adiposity and subclinical atherosclerosis.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Jul;29(7):728-735. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.03.010. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31138500
-
Markers of Early Vascular Ageing.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(22):3200-3204. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170328142433. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28356037 Review.
-
The effects of exercise on vascular markers and C-reactive protein among obese children and adolescents: An evidence-based review.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020 May 1;20(2):149-156. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2019.4345. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31509733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between C10X polymorphism in the CARD8 gene and inflammatory markers in young healthy individuals in the LBA study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Feb 13;24(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03765-7. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38350853 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of cardiorespiratory fitness and body composition on resting and post-exercise indices of vascular health in young adults.Sports Med Health Sci. 2023 Nov 21;6(1):54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.smhs.2023.11.003. eCollection 2024 Mar. Sports Med Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38463670 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin, CRP, and adiponectin correlate with body fat percentage in adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 11;12:1560080. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1560080. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40717997 Free PMC article.
-
Higher pulse wave velocity in young adult offspring of mothers with type 1 diabetes: a case-control study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Sep 6;21(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01612-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36068528 Free PMC article.
-
CRP levels are significantly associated with CRP genotype and estrogen use in The Lifestyle, Biomarker and Atherosclerosis (LBA) study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Apr 15;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02610-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35428187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jalowiec DA, Hill JA. Myocardial infarction in the young and in women. Cardiovasc Clin. 1989;20(1):197–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

