Identification of bacterial pathogens in cultured fish with a custom peptide database constructed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
- PMID: 32046727
- PMCID: PMC7014616
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-020-2274-1
Identification of bacterial pathogens in cultured fish with a custom peptide database constructed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
Abstract
Background: The majority of infectious diseases of cultured fish is caused by bacteria. Rapid identification of bacterial pathogens is necessary for immediate management. The present study developed a custom Main Spectra Profile (MSP) database and validate the method using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for rapid identification of fish bacterial pathogens. Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus iniae, Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas veronii, and Edwardsiella tarda obtained from diseased fish were used as representative bacterial pathogens in this study. Bacterial peptides were extracted to create a Main Spectra Profile (MSP), and the MSPs of each bacterial species was added into the MALDI Biotyper database. Fifteen additional isolates of each bacterial species were tested to validate the utilized technique.
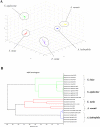
Results: The MSPs of all field isolates were clearly distinguishable, and the MSPs of the same species were clustered together. The identification methodology was validated with 75 bacterial isolates. The reliability and specificity of the method were determined with MALDI Biotyper log score values and matching results with 16 s rDNA sequencing. The species identification using the public MALDI Biotyper library (Bruker MALDI Biotyper) showed unreliable results (log score < 2.000) with 42.67% matching result with the reference method. In contrast, accurate identification was obtained when using the custom-made database, giving log score > 2.115, and a 100% matching result.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates an effective identification of fish bacterial pathogens when a complete custom-made MSP database is applied. Further applications require a broad, well-established database to accommodate prudent identification of many fish bacterial pathogens by MALDI-TOF MS.
Keywords: Biotyper; Fish disease; Mass spectrometry; Proteomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The optimization and validation of the Biotyper MALDI-TOF MS database for the identification of Gram-positive anaerobic cocci.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016 Sep;22(9):793-798. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 27404365
-
Rapid MALDI biotyper-based identification and cluster analysis of Streptococcus iniae.J Microbiol. 2017 Apr;55(4):260-266. doi: 10.1007/s12275-017-6472-x. Epub 2017 Jan 26. J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28124778
-
Development of a database for the rapid and accurate routine identification of Achromobacter species by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS).Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Jan;27(1):126.e1-126.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.031. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32283265
-
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) Analysis for the Identification of Pathogenic Microorganisms: A Review.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 19;9(7):1536. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071536. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34361971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Identification of Filamentous Fungi.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Nov 18;58(12):e01263-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01263-20. Print 2020 Nov 18. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32938733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A MALDI-TOF MS database for fast identification of Vibrio spp. potentially pathogenic to marine mollusks.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;105(6):2527-2539. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11141-0. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33590268 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus suis serotyping by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.PLoS One. 2021 May 4;16(5):e0249682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249682. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33945547 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of main spectral profile for rapid identification of Yersinia ruckeri isolated from Atlantic salmon using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Oct 20;9:1031373. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1031373. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36337185 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Strategies to Evaluate the Impact of Farming Conditions on Food Quality and Safety in Aquaculture Products.Foods. 2020 Aug 4;9(8):1050. doi: 10.3390/foods9081050. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32759674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of French Guiana anopheline mosquitoes by MALDI-TOF MS profiling using protein signatures from two body parts.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 20;15(8):e0234098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234098. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32817616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahoo P, Mukherjee S, Sahoo S. Aeromonas hydrophila versus Edwardsiella tarda: a pathoanatomical study in Clarias batrachus. J Aquacult. 1998;6:57–66.
-
- Jantrakajorn S, Maisak H, Wongtavatchai J. Comprehensive investigation of streptococcosis outbreaks in cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, and red tilapia, Oreochromis sp., of Thailand. J World Aquacult Soc. 2014;45(4):392–402. doi: 10.1111/jwas.12131. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

