Methylation silencing of TGF-β receptor type II is involved in malignant transformation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32046777
- PMCID: PMC7014638
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-020-0819-6
Methylation silencing of TGF-β receptor type II is involved in malignant transformation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Although massive studies have been conducted to investigate the mechanisms of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) carcinogenesis, the understanding of molecular alterations during the malignant transformation of epithelial dysplasia is still lacking, especially regarding epigenetic changes.
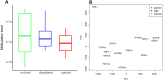
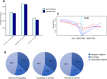
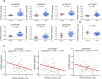
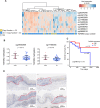
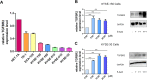
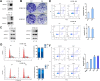
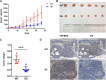
Results: To better characterize the methylation changes during the malignant transformation of epithelial dysplasia, a whole-genome bisulfite sequencing analysis was performed on a series of tumor, dysplastic, and non-neoplastic epithelial tissue samples from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients. Promoter hypermethylation in TGF-β receptor type II (TGFBR2), an important mediator of TGF-β signaling, was identified. Further, we evaluated the methylation and expression of TGFBR2 in tumor samples through The Cancer Genome Atlas multiplatform data as well as immunohistochemistry. Moreover, treatment of ESCC cell lines with5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine, a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, reactivated the expression of TGFBR2. The lentiviral mediating the overexpression of TGFBR2 inhibited the proliferation of ESCC cell line by inducing cell cycle G2/M arrest. Furthermore, the overexpression of TGFBR2 inhibited the tumor growth obviously in vivo.
Conclusions: The characterization of methylation silencing of TGFBR2 in ESCC will enable us to further explore whether this epigenetic change could be considered as a predictor of malignant transformation in esophageal epithelial dysplasia and whether use of a TGFBR2 agonist may lead to a new therapeutic strategy in patients with ESCC.
Keywords: Cancer diagnosis; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Methylation changes; TGFBR2; Treatment; Whole genome bisulfite sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic inactivation of secreted frizzled-related protein 2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Feb 14;18(6):532-40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.532. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22363119 Free PMC article.
-
Decitabine enhances tumor recognition by T cells through upregulating the MAGE-A3 expression in esophageal carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108632. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108632. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30797153
-
Epigenetic silencing of IGFBPL1 promotes esophageal cancer growth by activating PI3K-AKT signaling.Clin Epigenetics. 2020 Feb 10;12(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13148-020-0815-x. Clin Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32041673 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant DNA Methylation in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and its Clinical Implications in Systemic Chemotherapy.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 3;22(4):1002-1014. doi: 10.7150/ijms.109161. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39991775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The detective, prognostic, and predictive value of DNA methylation in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Apr 22;8:43. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0210-9. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27110300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of MTHFD2 as a novel prognosis biomarker in esophageal carcinoma patients based on transcriptomic data and methylation profiling.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 11;99(37):e22194. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022194. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32925794 Free PMC article.
-
GDF15 negatively regulates chemosensitivity via TGFBR2-AKT pathway-dependent metabolism in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Med. 2023 Feb;17(1):119-131. doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0949-7. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 36525138
-
Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in Cancer Immunology: Opportunities for Immunotherapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1408:309-328. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26163-3_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37093435 Review.
-
Transforming Growth Factor-β: A Multifunctional Regulator of Cancer Immunity.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 23;12(11):3099. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113099. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33114183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and Challenges in Targeting TGF-β Isoforms for Therapeutic Intervention of Cancer: A Mechanism-Based Perspective.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;17(4):533. doi: 10.3390/ph17040533. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

