Linc-OIP5 in the breast cancer cells regulates angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells through YAP1/Notch/NRP1 signaling circuit at a tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 32046779
- PMCID: PMC7014737
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-020-0273-0
Linc-OIP5 in the breast cancer cells regulates angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells through YAP1/Notch/NRP1 signaling circuit at a tumor microenvironment
Abstract
Background: LincRNAs have been revealed to be tightly associated with various tumorigeneses and cancer development, but the roles of specific lincRNA on tumor-related angiogenesis was hardly studied. Here, we aimed to investigate whether linc-OIP5 in breast cancer cells affects the angiogenesis of HUVECs and whether the linc-OIP5 regulations are involved in angiogenesis-related Notch and Hippo signaling pathways.
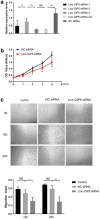
Methods: A trans-well system co-cultured HUVECs with linc-OIP5 knockdown breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 was utilized to study the proliferation, migration and tube formation abilities of HUVECs and alterations of related signaling indicators in breast cancer cells and their conditioned medium through a series of cell and molecular experiments.
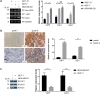
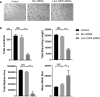
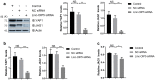
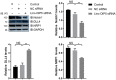
Results: Overexpressed linc-OIP5, YAP1, and JAG1 were found in breast cancer cell lines MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 and the expression levels of YAP1 and JAG1 were proportional to the breast cancer tissue grades. MDA-MB-231 cells with linc-OIP5 knockdown led to weakened proliferation, migration, and tube formation capacity of co-cultured HUVECs. Besides, linc-OIP5 knockdown in co-cultured MDA-MB-231 cells showed downregulated YAP1 and JAG1 expression, combined with a reduced JAG1 level in conditioned medium. Furthermore, a disrupted DLL4/Notch/NRP1 signaling in co-cultured HUVECs were also discovered under this condition.
Conclusion: Hence, linc-OIP5 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells may act on the upstream of the YAP1/Notch/NRP1 signaling circuit to affect proliferation, migration, and tube formation of co-cultured HUVECs in a non-cellular direct contact way through JAG1 in conditioned medium. These findings at least partially provide a new angiogenic signaling circuit in breast cancers and suggest linc-OIP5 could be considered as a therapeutic target in angiogenesis of breast cancers.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Breast cancer; HUVECs; Linc-OIP5; Signal transduction; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
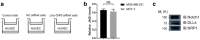
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

