Ascarids exposed: a method for in vitro drug exposure and gene expression analysis of anthelmintic naïve Parascaris spp
- PMID: 32046800
- PMCID: PMC10317622
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182020000189
Ascarids exposed: a method for in vitro drug exposure and gene expression analysis of anthelmintic naïve Parascaris spp
Abstract
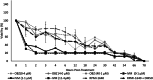
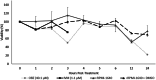
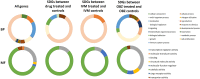
Ascarid parasites infect a variety of hosts and regular anthelmintic treatment is recommended for all species. Parascaris spp. is the only ascarid species with widespread anthelmintic resistance, which allows for the study of resistance mechanisms. The purpose of this study was to establish an in vitro drug exposure protocol for adult anthelmintic-naïve Parascaris spp. and report a preliminary transcriptomic analysis in response to drug exposure. Live worms were harvested from foal necropsies and maintained in RPMI-1640 at 37 °C. Serial dilutions of oxibendazole (OBZ) and ivermectin (IVM) were prepared for in vitro drug exposure, and worm viability was monitored over time. In a second drug trial, worms were used for transcriptomic analysis. The final drug concentrations employed were OBZ at 40.1 μm (10 μg mL-1) and IVM at 1.1 μm (1 μg mL-1) for 24 and 3 h, respectively. The RNA-seq analysis revealed numerous differentially expressed genes, with some being potentially related to drug detoxification and regulatory mechanisms. This report provides a method for in vitro drug exposure and the phenotypic responses for Parascaris spp., which could be extrapolated to other ascarid parasites. Finally, it also provides preliminary transcriptomic data following drug exposure as a reference point for future studies of Parascaris spp.
Keywords: Anthelmintic; Parascaris; ascarid; in vitro; transcriptome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional responses in Parascaris univalens after in vitro exposure to ivermectin, pyrantel citrate and thiabendazole.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Jul 9;13(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04212-0. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32646465 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin-induced gene expression changes in adult Parascaris univalens and Caenorhabditis elegans: a comparative approach to study anthelminthic metabolism and resistance in vitro.Parasit Vectors. 2022 May 5;15(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05260-4. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35513885 Free PMC article.
-
The equine ascarids: resuscitating historic model organisms for modern purposes.Parasitol Res. 2022 Oct;121(10):2775-2791. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07627-z. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 35986167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of parasiticidal activity of fenbendazole, ivermectin, oxibendazole, and pyrantel pamoate in horse foals with emphasis on ascarids (Parascaris equorum) in field studies on five farms in Central Kentucky in 2007.Parasitol Res. 2008 Jul;103(2):287-91. doi: 10.1007/s00436-008-0966-8. Epub 2008 May 10. Parasitol Res. 2008. PMID: 18470536
-
Anthelmintic resistance in equine parasites - detection, potential clinical relevance and implications for control.Vet Parasitol. 2012 Apr 19;185(1):2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.10.010. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Vet Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22100141 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene co-expression network analysis reveal core responsive genes in Parascaris univalens tissues following ivermectin exposure.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 15;19(2):e0298039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298039. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38359071 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional responses in Parascaris univalens after in vitro exposure to ivermectin, pyrantel citrate and thiabendazole.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Jul 9;13(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04212-0. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32646465 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin-induced gene expression changes in adult Parascaris univalens and Caenorhabditis elegans: a comparative approach to study anthelminthic metabolism and resistance in vitro.Parasit Vectors. 2022 May 5;15(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05260-4. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35513885 Free PMC article.
-
The P-glycoprotein repertoire of the equine parasitic nematode Parascaris univalens.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 12;10(1):13586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70529-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32788636 Free PMC article.
-
The equine ascarids: resuscitating historic model organisms for modern purposes.Parasitol Res. 2022 Oct;121(10):2775-2791. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07627-z. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 35986167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong SK, Woodgate RG, Gough S, Heller J, Sangster NC and Hughes KJ (2014) The efficacy of ivermectin, pyrantel and fenbendazole against Parascaris equorum infection in foals on farms in Australia. Veterinary Parasitology 205, 575–580. - PubMed
-
- Chelladurai JJ and Brewer MT (2019) Detection and quantification of Parascaris P-glycoprotein drug transporter expression with a novel mRNA hybridization technique. Veterinary Parasitology 267, 75–83. - PubMed
-
- Cvilink V, Lamka J and Skálová L (2009) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and metabolism of anthelmintics in helminths. Drug Metabolism Reviews 41, 8–26. - PubMed
-
- Feyereisen R (1999) Insect P450 enzymes. Annual Review of Entomology 44, 507–533. - PubMed

