Incubation period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travellers from Wuhan, China, 20-28 January 2020
- PMID: 32046819
- PMCID: PMC7014672
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.5.2000062
Incubation period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travellers from Wuhan, China, 20-28 January 2020
Abstract
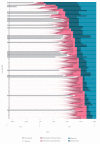
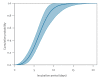
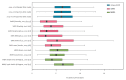
A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) is causing an outbreak of viral pneumonia that started in Wuhan, China. Using the travel history and symptom onset of 88 confirmed cases that were detected outside Wuhan in the early outbreak phase, we estimate the mean incubation period to be 6.4 days (95% credible interval: 5.6-7.7), ranging from 2.1 to 11.1 days (2.5th to 97.5th percentile). These values should help inform 2019-nCoV case definitions and appropriate quarantine durations.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; Wuhan; exposure; incubation period; novel coronavirus; symptom onset.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Statement Regarding Cluster of Pneumonia Cases in Wuhan, China. Beijing: WHO; 9 Jan 2020. [Accessed 26 Jan 2020]. https://www.who.int/china/news/detail/09-01-2020-who-statement-regarding...
-
- Imai N, Dorigatti I, Cori A, Donnelly C, Riley S, Ferguson NM. Report 2: Estimating the potential total number of novel Coronavirus cases in Wuhan City, China. London; 2020. Available from: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/sph/ide/gida-...
-
- Leung K, Wu JT, Leung GM. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet. 31 Jan 2020. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30260... - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
