Aspergillus fumigatus Infection in Humans With STAT3-Deficiency Is Associated With Defective Interferon-Gamma and Th17 Responses
- PMID: 32047500
- PMCID: PMC6997434
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00038
Aspergillus fumigatus Infection in Humans With STAT3-Deficiency Is Associated With Defective Interferon-Gamma and Th17 Responses
Abstract
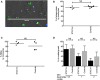
In humans, loss-of-function mutation in the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) gene is frequently associated with susceptibility to bacterial as well as fungal infections including aspergillosis, although its pathogenesis remains largely unknown. In the present study, we investigated the immune responses obtained after stimulation with Aspergillus fumigatus in STAT3-deficient patients. A. fumigatus conidial killing efficiencies of both monocytes and neutrophils isolated from whole blood samples of STAT3-deficient patients were not different compared to those of healthy controls. After stimulation with A. fumigatus conidia, lower concentrations of adaptive cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-17 and IL-22) were secreted by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from STAT3-deficient patients compared to those from healthy controls. Moreover, the frequency of IFN-γ and IL-17 producing CD4+ T cells was lower in STAT3-deficient patients vs. healthy controls. Among the STAT3-deficient patients, those with aspergillosis showed further lower secretion of IFN-γ upon stimulation of their PBMCs with A. fumigatus conidia compared to the patients without aspergillosis. Together, our study indicated that STAT3-deficiency leads to a defective adaptive immune response against A. fumigatus infection, particularly with a lower IFN-γ and IL-17 responses in those with aspergillosis, suggesting potential therapeutic benefit of recombinant IFN-γ in STAT3-deficient patients with aspergillosis.
Keywords: Aspergillus; IgE; IgG; aspergillosis; autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome (AD-HIES); innate/adaptive immunity; loss-of-function mutation; signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3).
Copyright © 2020 Danion, Aimanianda, Bayry, Duréault, Wong, Bougnoux, Tcherakian, Alyanakian, Guegan, Puel, Picard, Lortholary, Lanternier and Latgé.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impaired T cell responsiveness to interleukin-6 in hematological patients with invasive aspergillosis.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 2;10(4):e0123171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123171. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25835547 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of T-cell responses to Aspergillus fumigatus antigens in healthy individuals and patients with hematologic malignancies.Blood. 2002 Dec 15;100(13):4521-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-01-0265. Epub 2002 Aug 1. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12393638
-
The IL-36 receptor pathway regulates Aspergillus fumigatus-induced Th1 and Th17 responses.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Feb;43(2):416-26. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242711. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23147407
-
Clinical Manifestations and Genetic Analysis of 17 Patients with Autosomal Dominant Hyper-IgE Syndrome in Mainland China: New Reports and a Literature Review.J Clin Immunol. 2017 Feb;37(2):166-179. doi: 10.1007/s10875-017-0369-7. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28197791 Review.
-
The innate immune response to Aspergillus fumigatus at the alveolar surface.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015 Sep;39(5):670-87. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv018. Epub 2015 Apr 30. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25934117 Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporating the Detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated With Invasive Aspergillosis Into the Clinic.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Apr 12;12:860779. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.860779. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35601092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Governs the Host Inflammatory Response to Invasive Aspergillosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 10:2024.09.10.612305. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.10.612305. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2024 Dec 11;15(12):e0267124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02671-24. PMID: 39314401 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling governs the host inflammatory response to invasive aspergillosis.mBio. 2024 Dec 11;15(12):e0267124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02671-24. Epub 2024 Oct 30. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39475281 Free PMC article.
-
Human-Fungal Pathogen Interactions from the Perspective of Immunoproteomics Analyses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3531. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063531. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT-3 is necessary for IL-27-mediated macrophage suppression but does not represent a therapeutic target for E. coli-induced neonatal sepsis.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 25;13(5):e0221124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02211-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40130859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raz R, Durbin JE, Levy DE. Acute phase response factor and additional members of the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 family integrate diverse signals from cytokines, interferons, and growth factors. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:24391–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

