Kanglaite Injection Combined with Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy Alone for the Improvement of Clinical Efficacy and Immune Function in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32047528
- PMCID: PMC7007744
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8586596
Kanglaite Injection Combined with Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy Alone for the Improvement of Clinical Efficacy and Immune Function in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
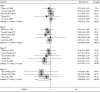
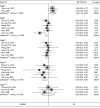
Recent advances have shown that immune checkpoint inhibitors are emerging as promising therapeutic targets to improve the quality of life in cancer patients. This meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the influence of Kanglaite injection (KLTi) combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone on clinical efficacy, immune function, and safety for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Several electronic databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Wan-Fang, VMIS, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CNKI, CBM, and MEDLINE, as well as grey literatures, were comprehensively searched from January 2000 to November 2019. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reporting outcomes of clinical efficacy and immune function were collected according to their inclusion and exclusion criteria. Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 5.2 was applied to assess the risk of bias of included trials. STATA 13.0 and Review Manager 5.3 software were used for meta-analysis. Twenty-five RCTs comprising 2151 patients meeting the inclusion criteria were identified. Meta-analysis showed that compared with chemotherapy alone, KLTi plus the same chemotherapy significantly improved clinical efficacy, including complete response, partial response, stable disease, and progressive disease, as well as immune function, including CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+. There was a significant reduction in nausea and vomiting, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia in combination treatments. However, the outcomes were limited because of the low quality and small sample size of the included studies. In conclusion, this work might provide beneficial evidence of KLTi combined with chemotherapy for improving clinical efficacy and immune function, as well as reducing the incidence of adverse events in advanced NSCLC patients. KLTi might be a beneficial therapeutic method for the treatment of advanced NSCLC. Due to the quality of the data, more rigorous and well-designed RCTs are needed to confirm these findings.
Copyright © 2020 Jianxia Wen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety for Kanglaite Injection in the Control of the Malignant Pleural Effusions via Thoracic Perfusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 3;12:694129. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.694129. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chinese patent medicine Kanglaite injection for non-small-cell lung cancer: An overview of systematic reviews.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;302(Pt A):115814. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115814. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36240975 Review.
-
Kanglaite injection plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for non-small cell lung cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2008 Oct;69(5):381-411. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2008.10.004. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2008. PMID: 24692815 Free PMC article.
-
Kanglaite injection plus platinum-based chemotherapy for stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of 27 RCTs.Phytomedicine. 2020 Feb;67:153154. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153154. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 31926475
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of Tanreqing injection combined with antibiotics versus antibiotics alone in the treatment of pulmonary infection patients after chemotherapy with lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phytother Res. 2021 Jan;35(1):122-137. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6790. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 32780543
Cited by
-
Coix seed oil regulates mitochondrial functional damage to induce apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer cells via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):5897-5909. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07371-8. Epub 2022 May 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35543827
-
Kanglaite Combined With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy for Stage III/IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A PRISMA-Compliant Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 13;12:739843. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.739843. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34588988 Free PMC article.
-
Low-grade fever during COVID-19 convalescence: A report of 3 cases.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Jun 26;8(12):2655-2661. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2655. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 32607346 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of first-line chemotherapy with Kanglaite injections versus first-line chemotherapy alone for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: study protocol for an investigator-initiated, multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Mar 17;22(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05169-w. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33731199 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma Cytokines and Metabolites Shows an Association between Galectin-9 and Changes in Peripheral Lymphocyte Subset Percentages Following Coix Seed Consumption.Nutrients. 2022 Apr 19;14(9):1696. doi: 10.3390/nu14091696. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35565664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NCCN. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®): Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Fort Washington, PA, USA: NCCN; 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

