Data Mining-Based Analysis of Chinese Medicinal Herb Formulae in Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment
- PMID: 32047530
- PMCID: PMC7003280
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9719872
Data Mining-Based Analysis of Chinese Medicinal Herb Formulae in Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has long been used to treat chronic kidney disease (CKD) in Asia. Its effectiveness and safety for CKD treatment have been confirmed in documented studies. However, the prescription rule of formulae for Chinese medicinal herbs is complicated and remains uncharacterized. Thus, we used data mining technology to evaluate the treatment principle and coprescription pattern of these formulae in CKD TCM treatment.
Methods: Data on patients with CKD were obtained from the outpatient system of a TCM hospital. We established a Chinese herb knowledge base based on the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and the Chinese Materia Medica. Then, following extraction of prescription information, we deweighted and standardized each prescribed herb according to the knowledge base to establish a database of CKD treatment formulae. We analyzed the frequency with which individual herbs were prescribed, as well as their properties, tastes, meridian tropisms, and categories. Then, we evaluated coprescription patterns and assessed medication rules by performing association rule learning, cluster analysis, and complex network analysis.
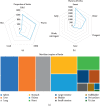
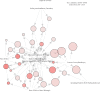
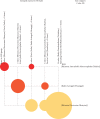
Results: We retrospectively analyzed 299 prescriptions of 166 patients with CKD receiving TCM treatment. The most frequently prescribed core herbs for CKD treatment were Rhizoma Dioscoreae (Shanyao), Spreading Hedyotis Herb (Baihuasheshecao), Root of Snow of June (Baimagu), Radix Astragali (Huangqi), Poria (Fulin), Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae (Baizhu), Radix Pseudostellariae (Taizishen), and Fructus Corni (Shanzhuyu). The TCM properties of the herbs were mainly being warm, mild, and cold. The tastes of the herbs were mainly sweet, followed by bitter. The main meridian tropisms were Spleen Meridian of Foot-Taiyin, Liver Meridian of Foot-Jueyi, Lung Meridian of Hand-Taiyin, Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming, and Kidney Meridian of Foot-Shaoyin. The top three categories were deficiency-tonifying, heat-clearing, and dampness-draining diuretic.
Conclusion: Using an integrated analysis method, we confirmed that the primary TCM pathogeneses of kidney disease were deficiency and dampness-heat. The primary treatment principles were tonifying deficiency and eliminating dampness-heat.
Copyright © 2020 Ping Xia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Data Mining-Based Study on Medication Rules of Chinese Herbs to Treat Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.Chin J Integr Med. 2022 Sep;28(9):847-854. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-2892-5. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Chin J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 35829954 Review.
-
Analysis on oral medication rules of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions for prevention of COVID-19.Chin Herb Med. 2021 Oct;13(4):502-517. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2021.10.007. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Chin Herb Med. 2021. PMID: 34659385 Free PMC article.
-
A Data Mining-Based Analysis of Core Herbs on Different Patterns (Zheng) of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 28;2021:3621677. doi: 10.1155/2021/3621677. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34257676 Free PMC article.
-
A Data Mining-Based Analysis of Medication Rules in Treating Bone Marrow Suppression by Kidney-Tonifying Method.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Feb 3;2019:1907848. doi: 10.1155/2019/1907848. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30854004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Study on drug properties and syndrome-symptom-formula-herb network of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of effort angina pectoris based on data visualization].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Sep;45(18):4482-4489. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200115.504. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33164379 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Jian-Pi-Yi-Shen Formula Ameliorates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis by Activating the Nrf2 Signaling in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;12:630210. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.630210. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33841151 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking-based characterization of the mechanisms through which Astragali Radix-Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz herb pair can treat membranous nephropathy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 6;104(23):e42785. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042785. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40489804 Free PMC article.
-
Lyophilized powder of calf bone marrow hydrolysate liposomes improved renal anemia: In vitro and in vivo evaluation.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 26;19(12):e0314811. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314811. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39724079 Free PMC article.
-
Design of an artificial neural network to predict mortality among COVID-19 patients.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;31:100983. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.100983. Epub 2022 May 29. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35664686 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between protein expression profiling of inflammation and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Sep;23(3):624-634. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i3.73. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38357138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foreman K. J., Marquez N., Dolgert A., et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. The Lancet. 2017;392(10159):2052–2090. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31694-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

