MicroRNA-183 in Cancer Progression
- PMID: 32047538
- PMCID: PMC6995398
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.39044
MicroRNA-183 in Cancer Progression
Abstract
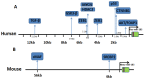
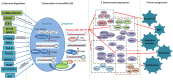
MicroRNA-183(miR-183) is abnormally expressed in many kinds of tumors. It participates in the initiation and development of tumors. There are many pathways regulate the expression of miR-183. The action mechanism of miR-183 in cancer is very extensive, and contradictory conclusions are often drawn. It was upregulated in 18 kinds of cancer, downregulated in 6 kinds of cancer. In addition, there are seven types of cancer, both upregulated and downregulated reports can be found. Evidence showed that miR-183 can not only directly play the role of oncogene or antioncogene, but also regulate the expression of other oncogene or antioncogene in different cancer types. In this review, we discuss the regulator of miR-183 and summarized the expression of miR-183 in different cancers. We also counted the target genes of miR-183 and the functional roles they play. Furthermore, we focused on the roles of miR-183 in cell migration, cell invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and microangiogenesis, which play the most important roles in cancer processes. It sheds light on the likely reasons why miR-183 plays different roles in various cancers. In addition, miR-183 and its downstream effectors have the potential to be promising prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in cancer.
Keywords: EMT; cancer progression; metastasis; microRNA-183; microangiogenesis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-34a targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):21362-21379. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15214. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423483 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer metastasis.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jul;51(1):235-244. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3999. Epub 2017 May 16. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534966
-
microRNA-33a prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through the Snail/Slug pathway.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):G147-G160. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00284.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30943047
-
MicroRNA-381-A Key Transcriptional Regulator: Its Biological Function and Clinical Application Prospects in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 26;10:535665. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.535665. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33324542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of MicroRNA-34a in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Competing Endogenous RNA Sponging and Its Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16;20(4):861. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040861. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-183-5p Promotes HCC Migration/Invasion via Increasing Aerobic Glycolysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Jun 4;14:3649-3658. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S304117. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34113130 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-183 cluster: a promising biomarker and therapeutic target in gastrointestinal malignancies.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;13(12):6147-6175. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38187051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer-Advances and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;24(17):13340. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713340. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miR-183 Cluster: Biogenesis, Functions, and Cell Communication via Exosomes in Cancer.Cells. 2023 May 5;12(9):1315. doi: 10.3390/cells12091315. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An imbalance between proliferation and differentiation underlies the development of microRNA-defective pineoblastoma.Genes Dev. 2025 Jun 2;39(11-12):727-750. doi: 10.1101/gad.352485.124. Genes Dev. 2025. PMID: 40240142
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

