Serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Human Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 32047539
- PMCID: PMC6995378
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.38048
Serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Human Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
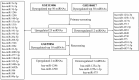
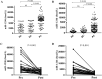
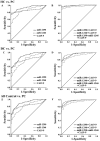
Background: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a highly malignant tumor with no effective early diagnostic biomarkers. This study was performed to screen and identify serum microRNAs (miRNAs) as noninvasive biomarkers for PC diagnosis. Methods: Two upregulated miRNAs were selected by integrated analysis of three independent GEO datasets. Then, the expressions of two miRNAs in serum were determined by quantitative reverse-transcription PCR among 120 PC patients, 40 benign disease controls and 40 healthy controls. The correlation between serum miRNAs and clinical characteristics was analyzed. The diagnostic utility of miRNAs was compared to CA19-9 using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Results: We discovered miR-1290 and miR-1246 were upregulated in PC patients through GEO datasets analysis. Serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 expression levels were elevated in PC patients compared to all controls and dramatically decreased after tumor resection (all P<0.001). The area under the curve (AUC) for miR-1290 was larger than miR-1246 and CA19-9 (miR-1290: 0.91; miR-1246: 0.81; CA19-9: 0.82). The combined diagnosis of individual or both miRNAs with CA19-9 was more effective for discriminating PC from all controls than the single CA19-9 assay (miR-1290+CA19-9: 0.96, miR-1246+CA19-9: 0.93, miR-1290+miR-1246+CA19-9: 0.97). The abundance of serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 was associated with tumor stage and size respectively and logistic modeling proved that both of them were independent risk factors for PC. Conclusion: Serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 might be promising biomarkers for PC diagnosis and the combined detection of CA19-9, together with miR-1290 or miR-1246, could improve the diagnostic accuracy of PC.
Keywords: diagnostic biomarker; pancreatic cancer; serum miRNA.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of plasma microRNAs with serum CA19-9 for early detection of pancreatic cancer.Int J Cancer. 2012 Aug 1;131(3):683-91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26422. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21913185
-
Trefoil factor(s) and CA19.9: A promising panel for early detection of pancreatic cancer.EBioMedicine. 2019 Apr;42:375-385. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.056. Epub 2019 Apr 5. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30956167 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of microRNAs in serum may identify individuals with pancreatic cancer.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Dec 15;7(12):5226-34. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25664025 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utilization of serum- or plasma-based miRNAs as early detection biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis up to now.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(35):e12132. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012132. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30170450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Sep 1;34(9):891-904. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002415. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35913776
Cited by
-
Early screening and diagnosis strategies of pancreatic cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Dec;41(12):1257-1274. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12204. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34331845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic methods for pancreatic cancer and their clinical applications (Review).Oncol Lett. 2025 May 27;30(1):370. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15116. eCollection 2025 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40496545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Approaches Using Body Fluid for the Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;11(2):375. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11020375. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of miRNAs for the Radiation Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;12(12):3703. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123703. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33317198 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-1246 Inhibits NFATc1 Phosphorylation and Regulates T Helper 17 Cell Activation in the Pathogenesis of Severe Alopecia Areata.Ann Dermatol. 2023 Feb;35(1):46-55. doi: 10.5021/ad.22.126. Ann Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36750458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Wood LD, Itoi T. et al. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Crawley AS, O'Kennedy RJ. The need for effective pancreatic cancer detection and management: a biomarker-based strategy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015;15:1339–1353. - PubMed
-
- Mizunoa N, Haraa K, Hijiokaa S. et al. Current concept of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2011;11(Suppl 2):40–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

