Long non-coding RNA TCL6 enhances preferential toxicity of paclitaxel to renal cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 32047545
- PMCID: PMC6995388
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.32552
Long non-coding RNA TCL6 enhances preferential toxicity of paclitaxel to renal cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
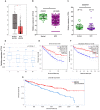
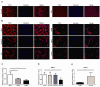
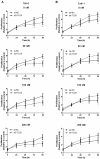
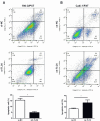
Background: Recent findings have shown long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are dysregulated in a variety of cancer cells. In this report, we investigate the effect of T-cell leukemia lymphoma 6 (TCL6) on paclitaxel (PTX)-induced apoptosis in Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells. Methods: Expression levels of TCL6 in RCC tissues were analyzed via The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed to detect the expression of TCL6 in RCC tissues and cells. Two pairs of cell lines were used: TCL6-silenced 786-O cell line and scrambled 786-O cell line, TCL6-overexpressed Caki-1 cell line and Caki-1 scrambled cell line. Cell viability was detected using the MTT assay. Apoptosis was examined by flow cemetery. Dual reporter gene assay was performed to confirm the direct downstream target miRNA of TCL6. Results: Based on RNA sequencing expression data of RCC tissues from TCGA and GEO datasets, the expression deficiency of TCL6 was observed in RCC tissues. Low level of TCL6 was associated with worse overall and disease-free survival of RCC patients. The FISH showed similar results with low expression of TCL6 in RCC tissues and cells. After PTX treatment, a time-dependent decrease in cell viability was observed in TCL6-overexpressed RCC cells and an increase in cell viability was observed in TCL6-silenced cells compared to control cells. Apoptosis induced by PTX was significantly increased in TCL6-overexpressed cells. Inhibition of TCL6 showed a significant decrease in apoptosis. Furthermore, luciferase reporter assay revealed that TCL6 is a direct target gene of miR-221. Conclusions: TCL6 effectively sensitizes RCC to PTX mainly through downregulation of miR-221. Our results suggest that PTX combined with TCL6 might be a potentially more effective chemotherapeutic approach for renal cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Chemotherapy.; Paclitaxel; Renal cell carcinoma.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Cho HY, Jacqmin D, Lee JE, Weikert S. et al. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2011;60:615–21. - PubMed
-
- Bechara GR, Júnior JADR, Gouveia HA, de Souza TAJOJoU. Metastasis to paranasal sinuses as the first presenting sign of renal cell carcinoma. Open Journal of Urology. 2012;2:28.
-
- Patard J-J, Leray E, Rioux-Leclercq N, Cindolo L, Ficarra V, Zisman A. et al. Prognostic value of histologic subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter experience. J Clin Oncol. 2004;23:2763–71. - PubMed
-
- Derosa L, Albiges L, Massard C, Loriot Y, Fizazi K, Escudier BJEoods. Safety of available treatment options for renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15:1097–106. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

