Downregulation of EVI1 Expression Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma via the PTEN/AKT Signalling Pathway
- PMID: 32047548
- PMCID: PMC6995371
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.31903
Downregulation of EVI1 Expression Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma via the PTEN/AKT Signalling Pathway
Abstract
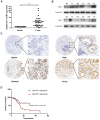
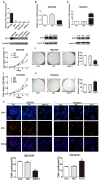
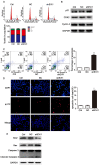
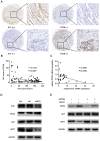
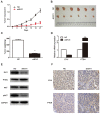
Aims: Hilar cholangiocarcinoma (HCCA) is a tumour with high malignancy, low surgical resection potential, and a poor prognosis. Ecotropic Viral Integration site 1 (EVI1) is a transcriptional regulator that has been proven to be associated with tumourigenesis and progression in many human solid tumours. However, the expression of EVI1 and its role in HCCA progression remain unclear. The aim of this study was to clarify the association between EVI1 expression and clinical outcomes in patients with HCCA. Methods: The expression of EVI1 in HCCA tissue samples and cell lines was examined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Kaplan-Meier analysis was used for survival analysis. A log-rank test was performed for univariate analysis of survival, and a Cox regression model was utilized for multivariate analysis of survival. Cell proliferation was measured by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), colony formation, and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays. The cell cycle was evaluated by flow cytometry. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labelling (TUNEL) assay. In vivo tumour growth was observed for xenografts in nude mice. Results: EVI1 expression was upregulated in HCCA tissue samples and correlated with a poor prognosis. In clinical specimens, the expression of EVI1 correlated with tumour histological grade and tumour size. Knocking down EVI1 expression reduced HCCA cell proliferation, blocked cell cycle progression, and promoted apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we found that EVI1 could regulate the AKT signalling pathway by regulating PTEN levels in HCCA. Conclusion: Our data revealed that EVI1 played important roles in HCCA tumourigenesis and development. Our findings suggest that EVI1 may be a potentially useful therapeutic target in HCCA.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; EVI1; Hilar cholangiocarcinoma; PTEN.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of tripartite motif 59 (TRIM59) inhibits proliferation in cholangiocarcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.044. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30822475
-
Tip60 Suppresses Cholangiocarcinoma Proliferation and Metastasis via PI3k-AKT.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(2):612-628. doi: 10.1159/000494183. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30308494
-
Dickkopf-1 expression is associated with tumorigenity and lymphatic metastasis in human hilar cholangiocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):70378-70387. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11859. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27608843 Free PMC article.
-
[EVI1 and its role in myelodysplastic syndrome, myeloid leukemia and other malignant diseases].Cas Lek Cesk. 2006;145(8):619-24. Cas Lek Cesk. 2006. PMID: 16995417 Review. Czech.
-
A Consensus Meeting on Expert Recommendations on Operating Specifications for Laparoscopic Radical Resection of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma.Front Surg. 2021 Nov 23;8:731448. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.731448. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34888342 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
KLF4 suppresses the proliferation of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma by negatively regulating GDF15 and phosphorylating AKT.Oncol Rep. 2023 Dec;50(6):222. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8659. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37937607 Free PMC article.
-
EVI1 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasive Properties of Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1050. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031050. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35162973 Free PMC article.
-
AKT inhibition sensitizes EVI1 expressing colon cancer cells to irinotecan therapy by regulating the Akt/mTOR axis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Aug;45(4):659-675. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00690-9. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 35834097
-
Epigenetic targeting of MECOM/KRAS axis by JIB-04 impairs tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance in MECOM-amplified ovarian cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 15;11(1):326. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02618-2. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40664642 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of bile biomarkers and their immunoregulatory role in biliary tract cancers.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 28;13:1049812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1049812. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doherty B, Nambudiri VE, Palmer WC. Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cholangiocarcinoma. Current gastroenterology reports. 2017;19:2. - PubMed
-
- LaFemina J, Jarnagin WR. Surgical management of proximal bile duct cancers. Langenbeck's archives of surgery. 2012;397:869–79. - PubMed
-
- Bird NTE, McKenna A, Dodd J, Poston G, Jones R, Malik H. Meta-analysis of prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with resected hilar cholangiocarcinoma. The British journal of surgery. 2018;105:1408–16. - PubMed
-
- Sano T, Shimada K, Sakamoto Y, Ojima H, Esaki M, Kosuge T. Prognosis of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: hilar bile duct cancer versus intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma involving the hepatic hilus. ANN SURG ONCOL/3655. 2008;15:590–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

