p16 promotes proliferation in cervical carcinoma cells through CDK6-HuR-IL1A axis
- PMID: 32047552
- PMCID: PMC6995400
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.35479
p16 promotes proliferation in cervical carcinoma cells through CDK6-HuR-IL1A axis
Abstract
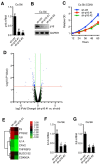
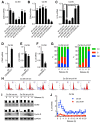
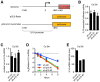
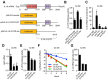
The Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p16 (p16) acts as a tumor suppressor in most cells, but for HPV transformed cervical cancer, in which oncoprotein E7 expressed by human papillomavirus (HPV) mediates the degradation of retinoblastoma protein (Rb), p16 exhibits oncogenic activity. Our study was conducted to study the mechanism underling p16 mediated promoting effect of cell proliferation in cervical cancer cell lines. CCK8 assay and EdU incorporation were conducted to evaluate cell proliferation. Loss-of-function assay was used to silence p16 in Ca Ski and SiHa cells. Next, western blot, qPCR, RNA silencing, luciferase activity assay, run-on assay, mRNA stability assay, RNA immunoprecipitation, co-immunoprecipitation Immunofluorescence were performed to examine the interaction between CDK6, HuR, and IL1A mRNA in p16 mediated proliferation promoting effect. Our results showed that: (1) Silencing p16 inhibited the proliferation of cervical cancer cells by decreasing the half-life of IL1A mRNA in CDK6 dependent manner; (2) The stabilization of IL1A mRNA was regulated by HuR which could be inactivated by p16/CDK6 mediated phosphorylation at Ser202; (3) IL1A mediated the oncogenic activity of p16 in cervical carcinoma cell lines. In conclusion, p16 promotes proliferation in cervical carcinoma cells through CDK6-HuR-IL1A axis.
Keywords: Cervical carcinoma; Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6; Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p16; ELAV-Like Protein 1; Interleukin-1alpha..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TGF-beta-mediated cell cycle arrest of HPV16-immortalized human ectocervical cells correlates with decreased E6/E7 mRNA and increased p53 and p21(WAF-1) expression.Exp Cell Res. 2000 Aug 25;259(1):149-57. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.4953. Exp Cell Res. 2000. PMID: 10942587
-
Downregulation of p16(ink4a) inhibits cell proliferation and induces G1 cell cycle arrest in cervical cancer cells.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Jun;33(6):1577-85. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1731. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24714974
-
P16INK4A is required for cisplatin resistance in cervical carcinoma SiHa cells.Oncol Lett. 2015 Mar;9(3):1104-1108. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2814. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25663864 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 (INK4a) in replicative senescence of normal human fibroblasts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 26;93(24):13742-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.24.13742. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8943005 Free PMC article.
-
The physiology of p16(INK4A)-mediated G1 proliferative arrest.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000;33(2):189-97. doi: 10.1385/CBB:33:2:189. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 11325039 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comparative Study on the Accuracy and Efficacy Between Dalton and CINtec® PLUS p16/Ki-67 Dual Stain in Triaging HPV-Positive Women.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 24;11:815213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.815213. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35141154 Free PMC article.
-
Computational investigation and experimental validation of the molecular mechanism of Solanecio mannii aqueous roots extract against cervical cancer.PLoS One. 2025 May 30;20(5):e0323680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323680. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40446016 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analyses Indicate That Cathepsin G (CTSG) is a Potential Immune-Related Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC).Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Feb 25;14:1275-1289. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S293148. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33658795 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the RNA-binding protein family in gynecologic cancers.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3799-3821. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37693158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting HSP70-E7 Interaction With SHetA2: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Cervical Cancer.J Med Virol. 2024 Nov;96(11):e70088. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70088. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 39588793
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

