Relationship between meiotic behaviour and fertility in backcross-1 derivatives of the [(Gossypium hirsutum × G. thurberi)2 × G. longicalyx] trispecies hybrid
- PMID: 32047586
- PMCID: PMC7000483
- DOI: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v14i1.47231
Relationship between meiotic behaviour and fertility in backcross-1 derivatives of the [(Gossypium hirsutum × G. thurberi)2 × G. longicalyx] trispecies hybrid
Abstract
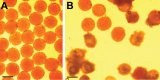
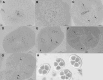
Wild cotton species are an important source of desirable genes for genetic improvement of cultivated cotton Gossypium hirsutum Linnaeus, 1763. For the success of such an improvement, chromosome pairings and recombinations in hybrids are fundamental. The wild African species G. longicalyx Hutchinson & Lee, 1958 could be used as donor of the desirable trait of fiber fineness. Twelve BC1 plants obtained from the backcrossing of [(G. hirsutum × G. thurberi Todaro, 1877)2 × G. longicalyx] (AhDhD1F1, 2n = 4x = 52) trispecies hybrid (HTL) by G. hirsutum (cv. C2) (AhAhDhDh, 2n = 4x = 52) were investigated for meiotic behaviour and plant fertility. Their chromosome associations varied as follows: (2.5 to 11.5) I + (17 to 22) II + (0.31 to 1.93) III + (0.09 to 1.93) IV + (0 to 0.07) V + (0 to 0.14) VI. Their pollen fertility ranged from 4.67 to 32.10 %. Only four BC1 plants produced a few seeds through self-pollination. The remaining BC1 were totally self-sterile and usually presented the highest number of univalents. All BC1 materials produced BC2 seeds (0.44 to 6.50 seeds per backcross) with the number of seeds negatively correlated with the number of univalents (R2 = 0.45, P < 0.05). Most BC1 plants gave significantly finer fiber compared to the cultivated G. hirsutum. SSR markers showed a segregation of wild alleles among the backcross derivatives and Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) revealed presence of entire chromosomes of G. longicalyx as well as recombinant chromosomes in the backcross derivatives. The significance and details of these results are presented and the prospects of successfully exploiting these plant materials are discussed.
Keywords: Gossypium spp; chromosome; cytogenetics; fiber fineness; hybrid; in situ hybridization; meiosis; plant breeding.
N’guessan Olivier Konan, Guy Mergeai.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Studies on the cytological characters of the interspecific hybrid F1 among the cultivated species in Gossypium and their genetic relationship.Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2005 Jul;32(7):744-52. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 16078744
-
Evaluation of cotton leaf curl virus resistance in BC1, BC2, and BC3 progenies from an interspecific cross between Gossypium arboreum and Gossypium hirsutum.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 5;9(11):e111861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111861. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25372141 Free PMC article.
-
Ten alien chromosome additions of Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium bickii developed by integrative uses of GISH and species-specific SSR markers.Mol Genet Genomics. 2018 Aug;293(4):945-955. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1434-5. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Mol Genet Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29589159
-
Characterization of eleven monosomic alien addition lines added from Gossypium anomalum to Gossypium hirsutum using improved GISH and SSR markers.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Oct 7;16(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0913-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27717331 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular cytogenetics, fertility, and scab resistance of the intergeneric hybrid F1 and BC1 between Triticum aestivum and Roegneria kamoji].Yi Chuan. 2009 Mar;31(3):290-6. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2009.00290. Yi Chuan. 2009. PMID: 19273443 Chinese.
References
-
- Abdelgadir HA, Johnson SD, Van Staden J. (2012) Pollen viability, pollen germination and pollen tube growth in the biofuel seed crop Jatropha curcas (Euphorbiaceae). South African Journal of Botany 79: 132–139. 10.1016/j.sajb.2011.10.005 - DOI
-
- Benbouza H, Jacquemin JM, Baudoin JP, Mergeai G. (2006) Optimization of a reliable, fast, cheap and sensitive silver staining method to detect SSR markers in polyacrylamide gels. Biotechnologie, Agronomie, Société et Environnement 2006 10: 77–81.
-
- Bikchurina TI, Tishakova KV, Kizilova EA, Romanenko SA, Serdyukova NA, Torgasheva AA, Borodin PM. (2018) Chromosome synapsis and recombination inmale-sterile and female-fertile interspecies hybrids of the dwarf hamsters (Phodopus cricetidae). Genes 9(5): 227 10.3390/genes9050227 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Menzel MY. (1950) New trispecies hybrids in cotton. Journal of Heredity 41: 291–295. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106063 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
