Distinctive structural properties of THB11, a pentacoordinate Chlamydomonas reinhardtii truncated hemoglobin with N- and C-terminal extensions
- PMID: 32048044
- PMCID: PMC7082302
- DOI: 10.1007/s00775-020-01759-2
Distinctive structural properties of THB11, a pentacoordinate Chlamydomonas reinhardtii truncated hemoglobin with N- and C-terminal extensions
Abstract
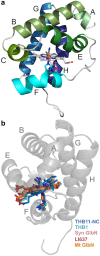
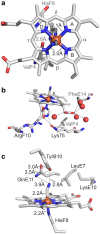
Hemoglobins (Hbs) utilize heme b as a cofactor and are found in all kingdoms of life. The current knowledge reveals an enormous variability of Hb primary sequences, resulting in topological, biochemical and physiological individuality. As Hbs appear to modulate their reactivities through specific combinations of structural features, predicting the characteristics of a given Hb is still hardly possible. The unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii contains 12 genes encoding diverse Hbs of the truncated lineage, several of which possess extended N- or C-termini of unknown function. Studies on some of the Chlamydomonas Hbs revealed yet unpredictable structural and biochemical variations, which, along with a different expression of their genes, suggest diverse physiological roles. Chlamydomonas thus represents a promising system to analyze the diversification of Hb structure, biochemistry and physiology. Here, we report the crystal structure, resolved to 1.75 Å, of the heme-binding domain of cyanomet THB11 (Cre16.g662750), one of the pentacoordinate algal Hbs, which offer a free Fe-coordination site in the reduced state. The overall fold of THB11 is conserved, but individual features such as a kink in helix E, a tilted heme plane and a clustering of methionine residues at a putative tunnel exit appear to be unique. Both N- and C-termini promote the formation of oligomer mixtures, and the absence of the C terminus results in reduced nitrite reduction rates. This work widens the structural and biochemical knowledge on the 2/2Hb family and suggests that the N- and C-terminal extensions of the Chlamydomonas 2/2Hbs modulate their reactivity by intermolecular interactions.
Keywords: Ligand tunnels; Nitrite reduction; Oligomerization; Pentacoordination; Truncated hemoglobin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of unusual truncated hemoglobins of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii suggests specialized functions.Planta. 2015 Jul;242(1):167-85. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2294-4. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Planta. 2015. PMID: 25893868
-
Characterization of THB1, a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii truncated hemoglobin: linkage to nitrogen metabolism and identification of lysine as the distal heme ligand.Biochemistry. 2014 Jul 22;53(28):4573-89. doi: 10.1021/bi5005206. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24964018 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine as a heme iron ligand: A property common to three truncated hemoglobins from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Dec;1862(12):2660-2673. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 30251657 Free PMC article.
-
Structural bases for heme binding and diatomic ligand recognition in truncated hemoglobins.J Inorg Biochem. 2005 Jan;99(1):97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.10.035. J Inorg Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15598494 Review.
-
Protein fold and structure in the truncated (2/2) globin family.Gene. 2007 Aug 15;398(1-2):2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.02.045. Epub 2007 Apr 29. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17532150 Review.
References
-
- Vinogradov SN, Hoogewijs D, Bailly X, Mizuguchi K, Dewilde S, Moens L, Vanfleteren JR. A model of globin evolution. Gene. 2007;398:132–142. - PubMed
-
- Vinogradov SN, Moens L. Diversity of globin function: enzymatic, transport, storage, and sensing. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:8773–8777. - PubMed
-
- Gell DA. Structure and function of haemoglobins. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2018;70:13–42. - PubMed
-
- Perutz MF, Kendrew JC, Watson HC. Structure and function of haemoglobin: II. Some relations between polypeptide chain configuration and amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol. 1965;13:669–678.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

