A Relative Cost of Control Analysis of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Exenatide Extended-Release, Dulaglutide and Liraglutide in the UK
- PMID: 32048148
- PMCID: PMC7089718
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-020-01242-z
A Relative Cost of Control Analysis of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Exenatide Extended-Release, Dulaglutide and Liraglutide in the UK
Abstract
Introduction: Once-weekly semaglutide 1 mg is a novel glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) that, in the SUSTAIN clinical trials, has demonstrated greater reductions in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and body weight than the other GLP-1 RAs exenatide extended-release (ER) 2 mg, dulaglutide 1.5 mg and liraglutide 1.2 mg. The aim of this analysis was to evaluate the relative cost of control of achieving treatment goals in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) treated with once-weekly semaglutide versus exenatide ER, dulaglutide and liraglutide from a UK perspective.
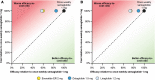
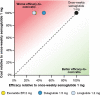
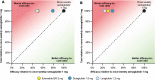
Methods: Proportions of patients reaching HbA1c targets (< 7.0% and < 7.5%), weight loss targets (≥ 5% reduction in body weight) and composite endpoints (HbA1c < 7.0% without weight gain or hypoglycaemia; reduction in HbA1c of ≥ 1% and weight loss of ≥ 5%) were obtained from the SUSTAIN clinical trials. Annual per patient treatment costs were based on wholesale acquisition costs from July 2019 in the UK. Cost of control was calculated by plotting relative treatment costs against relative efficacy.
Results: The annual per patient cost was similar for all GLP-1 RAs. Once-weekly semaglutide was superior to exenatide ER, dulaglutide and liraglutide in bringing patients to HbA1c and weight loss targets, and to composite endpoints. When looking at the composite endpoint of HbA1c < 7.0% without weight gain or hypoglycaemia, exenatide ER, dulaglutide and liraglutide were 50.0%, 21.6% and 51.3% less efficacious in achieving this, respectively, than once-weekly semaglutide. Consequently, the efficacy-to-cost ratios for once-weekly semaglutide were superior to all comparators in bringing patients to all endpoints.
Conclusions: The present study showed that once-weekly semaglutide offers superior cost of control versus exenatide ER, dulaglutide and liraglutide in terms of achieving clinically relevant, single and composite endpoints. Once-weekly semaglutide 1 mg would therefore represent good value for money in the UK setting.
Keywords: Cost of control analysis; Cost-effectiveness; Diabetes; Economic evaluation; Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists; Semaglutide; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Relative Cost of Control Analysis of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Exenatide Extended-Release and Dulaglutide for Bringing Patients to HbA1c and Weight Loss Treatment Targets in the USA.Adv Ther. 2019 May;36(5):1190-1199. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00915-8. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 30875029 Free PMC article.
-
Oral semaglutide versus injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a cost of control analysis.J Med Econ. 2020 Jun;23(6):650-658. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2020.1722678. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Med Econ. 2020. PMID: 31990244
-
Evaluating the Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Liraglutide for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in the UK.Adv Ther. 2020 May;37(5):2427-2441. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01337-7. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32306244 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Apr;19(4):524-536. doi: 10.1111/dom.12849. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 27981757
-
Efficacy and safety of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists compared with exenatide and liraglutide in type 2 diabetes: a systemic review of randomised controlled trials.Int J Clin Pract. 2016 Aug;70(8):649-56. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12847. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Int J Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 27456750
Cited by
-
Cost-Utility Analysis of Once-Weekly Semaglutide, Dulaglutide, and Exenatide for Type 2 Diabetes Patients Receiving Metformin-Based Background Therapy in China.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 18;13:831364. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.831364. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35250578 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of GLP1 on Body Weight and Glycemic Management in Patients with Diabetes-A Scientometric Investigation and Visualization Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Oct 27;60(11):1761. doi: 10.3390/medicina60111761. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39596946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long- and Short-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Once-Weekly Semaglutide versus Dulaglutide for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in China: A Hypothetical Modeling Exercise.Diabetes Ther. 2025 May;16(5):915-929. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01716-9. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40106226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Foundation. IDF diabetes atlas, 8th edn. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, United Kingdom country report 2017 and 2045. 2017. https://reports.instantatlas.com/report/view/704ee0e6475b4af885051bcec15.... Accessed Oct 2019.
-
- Diabetes UK. Us, diabetes and a lot of facts and stats. 2019. https://www.diabetes.org.uk/resources-s3/2019-02/1362B_Facts%20and%20sta.... Accessed Oct 2019.
-
- National Health Service. National diabetes audit, 2015–16. Report 2a: complications and mortality (complications of diabetes). 2017. https://files.digital.nhs.uk/pdf/4/t/national_diabetes_audit__2015-16__r.... Accessed Nov 2019.
-
- International Diabetes Foundation. IDF diabetes atlas, 8th edn. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation. 2017. http://www.diabetesatlas.org/. Accessed Sep 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

