The forgotten exotic tapeworms: a review of uncommon zoonotic Cyclophyllidea
- PMID: 32048575
- PMCID: PMC7174715
- DOI: 10.1017/S003118202000013X
The forgotten exotic tapeworms: a review of uncommon zoonotic Cyclophyllidea
Abstract
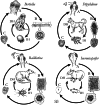
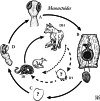
As training in helminthology has declined in the medical microbiology curriculum, many rare species of zoonotic cestodes have fallen into obscurity. Even among specialist practitioners, knowledge of human intestinal cestode infections is often limited to three genera, Taenia, Hymenolepis and Dibothriocephalus. However, five genera of uncommonly encountered zoonotic Cyclophyllidea (Bertiella, Dipylidium, Raillietina, Inermicapsifer and Mesocestoides) may also cause patent intestinal infections in humans worldwide. Due to the limited availability of summarized and taxonomically accurate data, such cases may present a diagnostic dilemma to clinicians and laboratories alike. In this review, historical literature on these cestodes is synthesized and knowledge gaps are highlighted. Clinically relevant taxonomy, nomenclature, life cycles, morphology of human-infecting species are discussed and clarified, along with the clinical presentation, diagnostic features and molecular advances, where available. Due to the limited awareness of these agents and identifying features, it is difficult to assess the true incidence of these 'forgotten' cestodiases as clinical misidentifications are likely to occur. Also, the taxonomic status of many of the human-infecting species of these tapeworms is unclear, hampering accurate species identification. Further studies combining molecular data and morphological observations are necessary to resolve these long-standing taxonomic issues and to elucidate other unknown aspects of transmission and ecology.
Keywords: Bertiella; Cestodes; Cyclophyllidea; Dipylidium; Inermicapsifer; Mesocestoides; Raillietina; Zoonoses.
Figures

References
-
- Achir I, Zait H and Hamrioui B (2008) Human infection due to Bertiella sp (Cestode: Anoplocephalidae) in a man originating from Yemen in Algeria. Bulletin de la Société de Pathologie Exotique 101, 107–108. - PubMed
-
- Adams A (1935) A fourth case of human infection with B. studeri (Cestoda) in Mauritius. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 29, 361–362.
-
- Adams A and Webb L (1933) Two further cases of human infestation with Bertiella studeri (Blanchard, 1891) Stiles and Hassall, 1902, with some observations on the probable synonymy of the specimens previously recorded from man. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 27, 471–475.
-
- Africa CM and Garcia EY (1935) The occurrence of Bertiella in man, monkey and dog in the Philippines. Philippine Journal of Science 56, 1–10.
-
- Al-Mathal E, Saleh N and Morsy T (2010) Human infection with Bertiella studeri (Cestode: Anoplocephalidae) in an Egyptian worker returning back from Saudi Arabia. Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology 40, 89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

