Early erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in preterm or low birth weight infants
- PMID: 32048730
- PMCID: PMC7014351
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004863.pub6
Early erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in preterm or low birth weight infants
Abstract
Background: Preterm infants have low plasma levels of erythropoietin (EPO), providing a rationale for the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to prevent or treat anaemia and to provide neuro protection and protection against necrotising enterocolitis (NEC). Darbepoetin (Darbe) and EPO are currently available ESAs.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness and safety of ESAs (erythropoietin (EPO) and/or Darbe) initiated early (before eight days after birth) compared with placebo or no intervention in reducing red blood cell (RBC) transfusions, adverse neurological outcomes, and feeding intolerance including necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) in preterm and/or low birth weight infants. Primary objective for studies that primarily investigate the effectiveness and safety of ESAs administered early in reducing red blood cell transfusions: To assess the effectiveness and safety of ESAs initiated early in reducing red blood cell transfusions in preterm infants. Secondary objectives: Review authors performed subgroup analyses of low (≤ 500 IU/kg/week) and high (> 500 IU/kg/week) doses of EPO and the amount of iron supplementation provided: none, low (≤ 5 mg/kg/d), and high (> 5 mg/kg/d). Primary objective for studies that primarily investigate the neuro protective effectiveness of ESAs: To assess the effectiveness and safety of ESAs initiated early in reducing adverse neurological outcomes in preterm infants. Primary objective for studies that primarily investigate the effectiveness of EPO or Darbe administered early in reducing feeding intolerance: To assess the effectiveness and safety of ESAs administered early in reducing feeding intolerance (and NEC) in preterm infants. Other secondary objectives: To compare the effectiveness of ESAs in reducing the incidence of adverse events and improving long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Search methods: We used the standard search strategy of Cochrane Neonatal to search the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2017, Issue 2), MEDLINE via PubMed (1966 to 10 March 2017), Embase (1980 to 10 March 2017), and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL; 1982 to 10 March 2017). We searched clinical trials databases, conference proceedings, and reference lists of retrieved articles for randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials.
Selection criteria: Randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials of early initiation of EAS treatment versus placebo or no intervention in preterm or low birth weight infants.
Data collection and analysis: We used the methods described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and the GRADE approach to assess the quality of evidence.
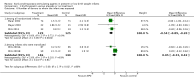
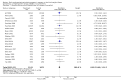
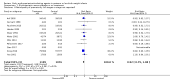
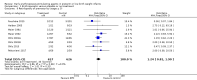
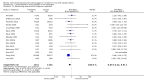
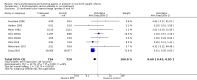
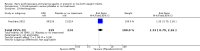
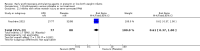
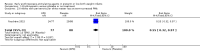
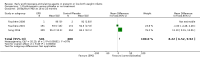
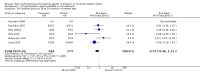
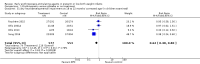
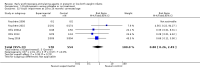
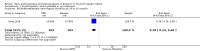
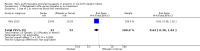
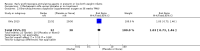
Main results: This updated review includes 34 studies enrolling 3643 infants. All analyses compared ESAs versus a control consisting of placebo or no treatment. Early ESAs reduced the risk of 'use of one or more [red blood cell] RBC transfusions' (typical risk ratio (RR) 0.79, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.74 to 0.85; typical risk difference (RD) -0.14, 95% CI -0.18 to -0.10; I2 = 69% for RR and 62% for RD (moderate heterogeneity); number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 7, 95% CI 6 to 10; 19 studies, 1750 infants). The quality of the evidence was low. Necrotising enterocolitis was significantly reduced in the ESA group compared with the placebo group (typical RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.52 to 0.91; typical RD -0.03, 95% CI -0.05 to -0.01; I2 = 0% for RR and 22% for RD (low heterogeneity); NNTB 33, 95% CI 20 to 100; 15 studies, 2639 infants). The quality of the evidence was moderate. Data show a reduction in 'Any neurodevelopmental impairment at 18 to 22 months' corrected age in the ESA group (typical RR 0.62, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.80; typical RD -0.08, 95% CI -0.12 to -0.04; NNTB 13, 95% CI 8 to 25. I2 = 76% for RR (high heterogeneity) and 66% for RD (moderate); 4 studies, 1130 infants). The quality of the evidence was low. Results reveal increased scores on the Bayley-II Mental Development Index (MDI) at 18 to 24 months in the ESA group (weighted mean difference (WMD) 8.22, 95% CI 6.52 to 9.92; I2 = 97% (high heterogeneity); 3 studies, 981 children). The quality of the evidence was low. The total volume of RBCs transfused per infant was reduced by 7 mL/kg. The number of RBC transfusions per infant was minimally reduced, but the number of donors to whom infants who were transfused were exposed was not significantly reduced. Data show no significant difference in risk of stage ≥ 3 retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) with early EPO (typical RR 1.24, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.90; typical RD 0.01, 95% CI -0.02 to 0.04; I2 = 0% (no heterogeneity) for RR; I2 = 34% (low heterogeneity) for RD; 8 studies, 1283 infants). Mortality was not affected, but results show significant reductions in the incidence of intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH) and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL).
Authors' conclusions: Early administration of ESAs reduces the use of red blood cell (RBC) transfusions, the volume of RBCs transfused, and donor exposure after study entry. Small reductions are likely to be of limited clinical importance. Donor exposure probably is not avoided, given that all but one study included infants who had received RBC transfusions before trial entry. This update found no significant difference in the rate of ROP (stage ≥ 3) for studies that initiated EPO treatment at less than eight days of age, which has been a topic of concern in earlier versions of this review. Early EPO treatment significantly decreased rates of IVH, PVL, and NEC. Neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18 to 22 months and later varied in published studies. Ongoing research should evaluate current clinical practices that will limit donor exposure. Promising but conflicting results related to the neuro protective effect of early EPO require further study. Very different results from the two largest published trials and high heterogeneity in the analyses indicate that we should wait for the results of two ongoing large trials before drawing firm conclusions. Administration of EPO is not currently recommended because limited benefits have been identified to date. Use of darbepoetin requires further study.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
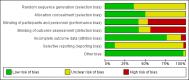
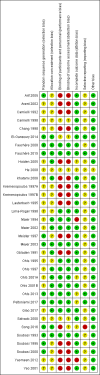
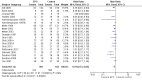












































































Update of
-
Early erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in preterm or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 16;11(11):CD004863. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004863.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 11;2:CD004863. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004863.pub6. PMID: 29145693 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arif 2005 {published data only}
Avent 2002 {published data only}
-
- Avent M, Cory BJ, Galpin J, Ballot DE, Cooper PA, Sherman G, et al. A comparison of high versus low dose recombinant human erythropoietin versus blood transfusion in the management of anaemia of prematurity in a developing country. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2002;48(4):227‐33. [PUBMED: 12200985] - PubMed
Carnielli 1992 {published data only}
-
- Carnielli V, Montini G, Riol R, Dall'Amico R, Cantarutti F. Effect of high doses of human recombinant erythropoietin on the need for blood transfusions in preterm infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;121(1):98‐102. [PUBMED: 1625101] - PubMed
Carnielli 1998 {published data only}
Chang 1998 {published data only}
-
- Chang L, Liu W, Liao C, Zhao X. Preventive effects of different dosages of recombinant human erythropoietin on anemia of premature infants. Journal of Tongji Medical University/Tong Ji Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao 1998;18(4):239‐42. [PUBMED: 10806855] - PubMed
El‐Ganzoury 2014 {published data only}
-
- El‐Ganzoury MM, Awad HA, El‐Farrash RA, El‐Gammasy TM, Ismail EA, Mohamed HE, et al. Enteral granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor and erythropoietin early in life improves feeding tolerance in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pediatrics 2014;165(6):1140‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.034; PUBMED: 25155966] - DOI - PubMed
Fauchère 2008 {published data only}
Fauchère 2015 {published data only}
-
- Fauchère JC, Koller BM, Tschopp A, Dame C, Ruegger C, Bucher HU, Swiss Erythropoietin Neuroprotection Trial Group. Safety of early high‐dose recombinant erythropoietin for neuroprotection in very preterm infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2015;167(1):52‐7.e1‐3. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.02.052; PUBMED: 25863661] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Natalucci G, Latal B, Koller B, Ruegger C, Sick B, Held L, et al. Swiss EPO Neuroprotection Trial Group. Effect of early prophylactic high‐dose recombinant human erythropoietin in very preterm infants on neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016;315(19):2079‐85. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2016.5504; PUBMED: 27187300] - DOI - PubMed
-
- O'Gorman RL, Bucher HU, Held U, Koller BM, Hűppi PS, Hagmann CF, et al. Swiss EPO Neuroprotection Trial Group. Tract‐based spatial statistics to assess the neuroprotective effect of early erythropoietin on white matter development in preterm infants. Brain 2015;138(Pt 2):388‐97. [DOI: 10.1093/brain/awu363; PUBMED: 25534356] - DOI - PubMed
Haiden 2005 {published data only}
-
- Haiden N, Cardona F, Schwindt J, Berger A, Kuhle S, Homoncik M, et al. Changes in thrombopoiesis and platelet reactivity in extremely low birth weight infants undergoing erythropoietin therapy for treatment of anaemia of prematurity. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2005;93(1):118‐23. [DOI: 10.1160/TH04-02-0093; PUBMED: 15630501] - DOI - PubMed
He 2008 {published data only}
-
- He JS, Huang ZL, Yang H, Weng KZ, Zhu SB. Early use of recombinant human erythropoietin promotes neurobehavioral development in preterm infants. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics] 2008;10(5):586‐8. [PUBMED: 18947475] - PubMed
Khatami 2008 {published data only}
Kremenopoulos 1997A {published data only}
-
- Kremenopoulos G, Soubasi V, Tsantali C, Diamanti E, Tsakiris D. The best timing of recombinant human erythropoietin administration in anemia of prematurity: a randomized controlled study. International Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology 1997;4(4):373‐83. [EMBASE: 1997362607]
Kremenopoulos 1997B {published data only}
-
- Kremenopoulos G, Soubasi V, Tsantali C, Diamanti E, Tsakiris D. The best timing of recombinant human erythropoietin administration in anemia of prematurity: a randomized controlled study. International Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology 1997;4(4):373‐83. [EMBASE: 1997362607]
Lauterbach 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lauterbach R, Kachlik P, Pawlik D, Bajorek I. Evaluation of treatment results for anemia of prematurity treated with various doses of human recombinant erythropoietin. Pediatria Polska 1995;70(9):739‐44. [PUBMED: 8657506] - PubMed
Lima‐Rogel 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lima‐Rogel V, Torres‐Montes A, Espinosa Griesse S, Villegas Alvarez C, Hernandez‐Sierra F, Bissett Mandeville P, et al. Efficacy of early erythropoietin use in critically ill very‐low‐birth‐weight premature newborn infants: controlled clinical trial [Eficacia del uso precoz de eritropoyetina en recien nacidos pretermino de muy bajo peso, criticamente enfermos: ensayo clinico controlado]. Sangre 1998;43(3):191‐5. [PUBMED: 9741224] - PubMed
Maier 1994 {published data only}
-
- Maier RF, Obladen M, Scigalla P, Linderkamp O, Duc G, Hieronimi G, et al. The effect of epoetin beta (recombinant human erythropoietin) on the need for transfusion in very‐low‐birth‐weight infants. European Multicentre Erythropoietin Study Group. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330(17):1173‐8. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199404283301701; PUBMED: 8139627] - DOI - PubMed
Maier 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Maier RF, Obladen M, Muller‐Hansen I, Kattner E, Merz U, Arlettaz R, et al. European Multicenter Erythropoietin Beta Study Group. Early treatment with erythropoietin beta ameliorates anemia and reduces transfusion requirements in infants with birth weights below 1000 g. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141(1):8‐15. [DOI: 10.1067/mpd.2002.124309; PUBMED: 12091844] - DOI - PubMed
Meister 1997 {published data only}
Meyer 2003 {published data only}
Obladen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Obladen M, Maier R, Segerer H, Grauel EL, Holland BM, Stewart G, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human erythropoietin to prevent the anaemias of prematurity. European randomized multicenter trial. Contributions to Nephrology 1991;88:314‐26. [PUBMED: 2040194] - PubMed
Ohls 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ohls RK, Osborne KA, Christensen RD. Efficacy and cost analysis of treating very low birth weight infants with erythropoietin during their first two weeks of life: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Pediatrics 1995;126(3):421‐6. [PUBMED: 7869205] - PubMed
Ohls 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ohls RK, Harcum J, Schibler KR, Christensen RD. The effect of erythropoietin on the transfusion requirements of preterm infants weighing 750 grams or less: a randomized, double blind, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Pediatrics 1997;131(5):661‐5. [PUBMED: 9403642] - PubMed
Ohls 2001A {published data only}
-
- Ehrenkranz RA, Ohls RK, Das A, Vohr BR. Neurodevelopmental outcome and growth at 18‐22 months in extremely low birth weight infants treated with early erythropoietin. Pediatric Research 2002;51:291A. - PubMed
-
- Ohls RK, Ehrenkranz RA, Das A, Dusick AM, Yolton K, Romano E, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome and growth at 18 to 22 months' corrected age in extremely low birth weight infants treated with early erythropoietin and iron. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):1287‐91. - PubMed
-
- Ohls RK, Ehrenkranz RA, Das A, Dusick AM, Yolton K, Romano E, et al. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neurodevelopmental outcome and growth at 18 to 22 months' corrected age in extremely low birth weight infants treated with early erythropoietin and iron. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):1287‐91. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2003-1129-L; PUBMED: 15520109] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ohls RK, Ehrenkranz RA, Lemons JA, Korones SB, Stoll BJ, Stark AR, et al. A multicenter randomized double‐masked placebo‐controlled trial of early erythropoietin and iron administration to preterm infants. Pediatric Research 1999;45:216A. - PubMed
-
- Ohls RK, Ehrenkranz RA, Wright LL, Lemons JA, Korones SB, Stoll BJ, et al. Effects of early erythropoietin therapy on the transfusion requirements of preterm infants below 1250 grams birth weight: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2001;108(4):934‐42. [PUBMED: 11581447] - PubMed
Ohls 2001B {published data only}
-
- Ohls RK, Ehrenkranz RA, Wright LL, Lemons JA, Korones SB, Stoll BJ, et al. Effects of early erythropoietin therapy on the transfusion requirements of preterm infants below 1250 grams birth weight: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2001;108(4):934‐42. [PUBMED: 11581447] - PubMed
Ohls 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ohls RK, Kamath‐Rayne BD, Christensen RD, Wiedmeier SE, Rosenberg A, Schrader R, et al. Neurocognitive outcomes at 18‐22 months corrected age are improved in preterm infants administered darbepoetin or erythropoietin. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual meeting 2013. 2013:E‐PAS2013:1165.5.
Peltoniemi 2017 {published data only}
Qiao 2017 {published data only}
Salvado 2000 {published data only}
-
- Salvado A, Ramolfo P, Escobar M, Nunez A, Aguayo I, Standen J, et al. Early erythropoietin use for the prevention of anemia in infant premature [Uso precoz de la eritropoyetina en la prevencion de la anemia del prematuro]. Revista Medica de Chile 2000;128(12):1313‐7. [PUBMED: 11227239] - PubMed
Song 2016 {published data only}
Soubasi 1993 {published data only}
-
- Soubasi V, Kremenopoulos G, Diamandi E, Tsantali C, Tsakiris D. In which neonates does early recombinant human erythropoietin treatment prevent anemia of prematurity? Results of a randomized, controlled study. Pediatric Research 1993;34(5):675‐9. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-199311000-00022; PUBMED: 8284109] - DOI - PubMed
Soubasi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Soubasi V, Kremenopoulos G, Diamanti E, Tsantali C, Sarafidis K, Tsakiris D. Follow‐up of very low birth weight infants after erythropoietin treatment to prevent anemia of prematurity. Journal of Pediatrics 1995;127(2):291‐7. [PUBMED: 7636658] - PubMed
Soubasi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Soubasi V, Kremenopoulos G, Tsantali C, Savopoulou P, Mussafiris C, Dimitrou M. Use of erythropoietin and its effects on blood lactate and 2,3‐diphosphoglycerate in premature neonates. Biology of the Neonate 2000;78(4):281‐7. [DOI: ; PUBMED: 11093007] - PubMed
Yasmeen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yasmeen BHN, Chowdhury MA, Hoque MM, Hossain MM, Jahan R, Aktar S. Effect of short term recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in the prevention of anemia of prematurity in very low birth weight infants. Bangladesh Medical Research Council Bulletin 2012;38(3):119‐23. [PUBMED: 23540189] - PubMed
Yeo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Yeo CL, Choo S, Ho LY. Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin on transfusion needs in preterm infants. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2001;37(4):352‐8. [PUBMED: 11532054] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Al Mofada 1994 {published data only}
-
- Al Mofada SM. Safety and efficacy of early erythropoietin administration to pre‐term infants: a preliminary report. Medical Science Research 1994;22(10):749‐50. [EMBASE: 1994345936]
Amin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Amin AA, Alzahrani DM. Efficacy of erythropoietin in premature infants. Saudi Medical Journal 2002;23(3):287‐90. [PUBMED: 11938417] - PubMed
Basiri 2015 {published data only}
-
- Basiri B, Shokouhi M, Pezeshki N, Torabian S. Beneficial erythropoietic effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in very low‐birth weight infants: a single‐center randomized double‐blinded placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Neonatology 2015;4(2):87‐90. [EMBASE: 2015952409]
Bierer 2006 {published data only}
Brown 1999 {published data only}
-
- Brown MS, Keith JF 3rd. Comparison between two and five doses a week of recombinant erythropoietin for anemia of prematurity: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 1999;104(2 Pt 1):210‐5. [PUBMED: 10428996] - PubMed
Costa 2013 {published data only}
Fearing 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fearing MK, Eades B, Martinez B, Wood N, Accardo L, Browning CA, et al. Cost effective use of recombinant erythropoietin (HuEPO) in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants for improved clinical outcomes. Pediatric Research 2002;51:310A.
Haiden 2006a {published data only}
-
- Haiden N, Schwindt J, Cardona F, Berger A, Klebermass K, Wald M, et al. Effects of a combined therapy of erythropoietin, iron, folate, and vitamin B12 on the transfusion requirements of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2006;118(5):2004‐13. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2006-1113; PUBMED: 17079573] - DOI - PubMed
Haiden 2006b {published data only}
-
- Haiden N, Klebermass K, Cardona F, Schwindt J, Berger A, Kohlhauser‐Vollmuth C, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of the effects of adding vitamin B12 and folate to erythropoietin for the treatment of anemia of prematurity. Pediatrics 2006;118(1):180‐8. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2005-2475; PUBMED: 16818564] - DOI - PubMed
Juul 2008 {published data only}
Klipp 2007 {published data only}
-
- Klipp M, Holzwarth AU, Poeschl JM, Nelle M, Linderkamp O. Effects of erythropoietin on erythrocyte deformability in non‐transfused preterm infants. Acta Paediatrica 2007;96(2):253‐6. [PUBMED: 17429915] - PubMed
Krallis 1999 {published data only}
-
- Krallis N, Cholevas V, Mavridis A, Georgiou I, Bourantas K, Andronikou S. Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin in preterm infants. European Journal of Haematology 1999;63(2):71‐6. [PUBMED: 10480285] - PubMed
López‐Catzín 2015 {published data only}
-
- López‐Catzín JF, Bolado‐García PB, Gamboa‐López GJ, Medina‐Escobedo CE, Cambranes‐Catzima LR. Decreased transfusions in preterm infants with anemia treated with erythropoietin [Disminución de transfusiones en prematuros con anemia tratados con eritropoyetina]. Revista Medica del Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social 2016;54(5):576‐80. [PUBMED: 27428338] - PubMed
Maggio 2007 {published data only}
-
- Maggio L, Scorrano A, Cota F, Gallini F, Romagnoli C, Zuppa AA. Randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of early recombinant erythropoietin administered to preterm infants by continuous intravenous versus subcutaneous route. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual Meeting 2007. 2007:E‐PAS2007:616315.9.
Maier 1998 {published data only}
-
- Maier RF, Obladen M, Kattner E, Natzschka J, Messer J, Regazzoni BM, et al. High‐versus low‐dose erythropoietin in extremely low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1998;132(5):866‐70. [PUBMED: 9602202] - PubMed
Ohls 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ohls RK, Veerman MW, Christensen RD. Pharmacokinetics and effectiveness of recombinant erythropoietin administered to preterm infants by continuous infusion in total parenteral nutrition solution. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;128(4):518‐23. [PUBMED: 8618186] - PubMed
Saeidi 2012 {published data only}
Soubasi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Soubasi V, Pouliou T, Tsantali C, Lithoxopoulou M, Drossou V, Kremenopoulos G. Is erythropoietin (EPO) a multifunctional tissue protective cytokine? Follow‐up of rHuEPO treated prematures. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual Meeting 2005. 2005:PAS 2005;57:164.
Soubasi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Soubasi V, Petridou S, Sarafidis K, Agathi T, Griva M, Drossou V. High dose of erythropoietin in premature neonates: short‐term outcomes. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual Meeting 2009. 2009:E‐PAS 2009;5506:105.
Turker 2005 {published data only}
Vázquez López 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vázquez López MÁ, Llamas MÁ, Galera R, Sanchez AR, Lendinez F, Gonzalez‐Ripoll M, et al. Comparison between one and three doses a week of recombinant erythropoietin in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Perinatology 2011;31(2):118‐24. [DOI: 10.1038/jp.2010.80; PUBMED: 20689518] - DOI - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT01378273 {published data only}
-
- NCT01378273. Preterm Erythropoietin Neuroprotection Trial (PENUT Trial). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01378273 (first received 20 June 2011).
NCT02550054 {published data only}
-
- NCT02550054. Erythropoietin in Premature Infants to Prevent Encephalopathy [Erythropoietin in Premature Infants to Prevent Encephalopathy: A Multi‐centre Randomized Blinded Controlled Study of the Efficacy of Erythropoietin in China]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02550054 (first received 04 September 2015).
Additional references
Aher 2006a
Aher 2006b
Aher 2012
Aher 2012a
Baer 2011
-
- Baer VL, Lambert DK, Henry E, Snow GL, Christensen RD. Red blood cell transfusion of preterm neonates with grade 1 intraventricular hemorrhage is associated with extension to a grade 3 or 4 hemorrhage. Transfusion 2011;51(9):1933‐9. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03081.x; PUBMED: 21382049] - DOI - PubMed
Bassler 2009
-
- Bassler D, Stoll BJ, Schmidt B, Asztalos EV, Roberts RS, Robertson CM, et al. Trial of Indomethacin Prophylaxis in Preterm Investigators. Using a count of neonatal morbidities to predict poor outcome in extremely low birth weight infants: added role of neonatal infection. Pediatrics 2009;123(1):313‐8. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2008-0377; PUBMED: 19117897] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Begg 1996
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996;276(8):637‐9. [PUBMED: 8773637] - PubMed
Blau 2011
-
- Blau J, Calo JM, Dozor D, Sutton M, Alpan G, Gamma EF. Transfusion‐related acute gut injury: necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight neonates after packed red blood cell transfusion. Journal of Pediatrics 2011;158(3):403‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.09.015; PUBMED: 21067771] - DOI - PubMed
Brown 1983
-
- Brown MS, Phibbs RH, Garcia JF, Dallman PR. Postnatal changes in erythropoietin levels in untransfused premature infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1983;103(4):612‐7. [PUBMED: 6194281] - PubMed
Brown 1990
-
- Brown MS, Berman ER, Luckey D. Prediction of the need for transfusion during anemia of prematurity. Journal of Pediatrics 1990;116(5):773‐8. - PubMed
Chou 2017
Cohen 1998
-
- Cohen A, Manno C. Transfusion practices in infants receiving assisted ventilation. Clinics in Perinatology 1998;25(1):97‐111. [PUBMED: 9523077] - PubMed
Dallman 1981
Dame 2001
-
- Dame C, Juul SE, Christensen RD. The biology of erythropoietin in the central nervous system and its neurotrophic and neuroprotective potential. Biology of the Neonate 2001;79(3‐4):228‐35. [DOI: ; PUBMED: 11275657] - PubMed
Dolfin 1983
-
- Dolfin T, Skidmore MB, Fong KW, Hoskins EM, Shennan AT. Incidence, severity, and timing of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhages in preterm infants born in a perinatal unit as detected by serial real‐time ultrasound. Pediatrics 1983;71(4):541‐6. [PUBMED: 6835737] - PubMed
Egrie 2001
Finch 1982
-
- Finch CA. Erythropoiesis, erythropoietin and iron. Blood 1982;60:1241‐6. [PUBMED: 6753967] - PubMed
Fischer 2017
Garcia 2002
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.. GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 06 March 2017. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015., 2015.
Hesse 1997
-
- Hesse L, Eberl W, Schlaud M, Poets CF. Blood transfusion. Iron load and retinopathy of prematurity. European Journal of Pediatrics 1997;156(6):465‐70. [PUBMED: 9208245] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Juul 1999
-
- Juul SE. Erythropoietin in the neonate. Current Problems in Pediatrics 1999;29(5):133‐49. [PUBMED: 10331138] - PubMed
Juul 2002
-
- Juul S. Erythropoietin in the central nervous system, and its use to prevent hypoxic‐ischemic brain damage. Acta Paediatrica Supplement 2002;91(438):36‐42. [PUBMED: 12477263] - PubMed
Juul 2012
Kirpalani 2012
Klaus 1986
-
- Klaus MH, Fanaroff AA. Care of the High‐risk Neonate. 3rd Edition. Philadelphia, London, Toronto: W.B. Saunders Campany, 1986.
Klaus 1987
-
- Klaus M, Fanaroff A. Asistencia del Recien Nacido de Alto Riesgo. 3rd Edition. Colombia: Panamericana, 1987.
Kotto‐Kome 2004
-
- Kotto‐Kome AC, Garcia MG, Calhoun DA, Christensen RD. Effect of beginning recombinant erythropoietin treatment within the first week of life, among very‐low‐birth‐weight neonates, on "early" and "late" erythrocyte transfusions: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Perinatology 2004;24(1):24‐9. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211018; PUBMED: 14726934] - DOI - PubMed
Kumral 2011
Limperopoulos 2010
Messier 2014
Neubauer 2010
Newton 1999
-
- Newton NR, Leonard CH, Piecuch RE, Phibbs RH. Neurodevelopmental outcome of prematurely born children treated with recombinant human erythropoietin in infancy. Journal of Perinatology 1999;19(6 Pt 1):403‐6. [PUBMED: 10685268] - PubMed
Ohls 2000
-
- Ohls RK. The use of erythropoietin in neonates. Clinics in Perinatology 2000;27(3):681‐96. [PUBMED: 10986635] - PubMed
Ohls 2002
Ohls 2013a
Patel 2015
Rangarajan 2014
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schmidt 2003
-
- Schmidt B, Asztalos EV, Roberts RS, Robertson CM, Sauve RS, Whitfield MF, et al. Trial of Indomethacin Prophylaxis in Preterms (TIPP) Investigators. Impact of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, brain injury, and severe retinopathy on the outcome of extremely low‐birth‐weight infants at 18 months: results from the trial of indomethacin prophylaxis in preterms. JAMA 2003;289(9):1124‐9. [PUBMED: 12622582] - PubMed
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editors. GRADE Working Group. GRADE Handbook for Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. Available from https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/handbook/handbook.html. Updated October 2013.
Shannon 1995a
-
- Shannon KM. Recombinant human erythropoietin in neonatal anemia. Clinics in Perinatology 1995;22(3):627‐40. [PUBMED: 8521685] - PubMed
Sharp 2017
Shiou 2011
-
- Shiou SR, Yu Y, Chen S, Ciancio MJ, Petrof EO, Sun J, et al. Erythropoietin protects intestinal epithelial barrier function and lowers the incidence of experimental neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2011;286(14):12123‐32. [DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.154625; PUBMED: 21262973] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Stockman 1978
-
- Stockman JA 3rd, Oski FA. Physiological anaemia of infancy and the anaemia of prematurity. Clinics in Haematology 1978;7(1):3‐18. [PUBMED: 657601] - PubMed
Stockman 1986
-
- Stockman JA 3rd. Anemia of prematurity. Current concepts in the issue of when to transfuse. Pediatric Clinics of North America 1986;33(1):111‐28. [PUBMED: 3513096] - PubMed
Strauss 1986
-
- Strauss RG. Current issues in neonatal transfusions. Vox Sanguinis 1986;51(1):1‐9. [PUBMED: 3526725] - PubMed
Vamvakas 2001
-
- Vamvakas EC, Strauss RG. Meta‐analysis of controlled clinical trials studying the efficacy of rHuEPO in reducing blood transfusions in the anemia of prematurity. Transfusion 2001;41(3):406‐15. [PUBMED: 11274599] - PubMed
Wang 2015
Warwood 2005
Whyte 2011
Widness 1996
-
- Widness JA, Seward VJ, Kromer IJ, Burmeiser LF, Bell EF, Strauss RG. Changing patterns of red blood cell transfusion in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129(5):680‐7. [PUBMED: 8917234] - PubMed
Xu 2014
Zhang 2013
References to other published versions of this review
Ohlsson 2006
Ohlsson 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

