Neurogranin stimulates Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II by suppressing calcineurin activity at specific calcium spike frequencies
- PMID: 32049957
- PMCID: PMC7041932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006991
Neurogranin stimulates Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II by suppressing calcineurin activity at specific calcium spike frequencies
Abstract
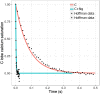
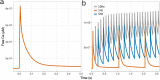
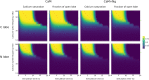
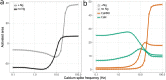
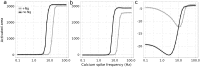
Calmodulin sits at the center of molecular mechanisms underlying learning and memory. Its complex and sometimes opposite influences, mediated via the binding to various proteins, are yet to be fully understood. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and calcineurin (CaN) both bind open calmodulin, favoring Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Depression (LTD) respectively. Neurogranin binds to the closed conformation of calmodulin and its impact on synaptic plasticity is less clear. We set up a mechanistic computational model based on allosteric principles to simulate calmodulin state transitions and its interactions with calcium ions and the three binding partners mentioned above. We simulated calcium spikes at various frequencies and show that neurogranin regulates synaptic plasticity along three modalities. At low spike frequencies, neurogranin inhibits the onset of LTD by limiting CaN activation. At intermediate frequencies, neurogranin facilitates LTD, but limits LTP by precluding binding of CaMKII with calmodulin. Finally, at high spike frequencies, neurogranin promotes LTP by enhancing CaMKII autophosphorylation. While neurogranin might act as a calmodulin buffer, it does not significantly preclude the calmodulin opening by calcium. On the contrary, neurogranin synchronizes the opening of calmodulin's two lobes and promotes their activation at specific frequencies. Neurogranin suppresses basal CaN activity, thus increasing the chance of CaMKII trans-autophosphorylation at high-frequency calcium spikes. Taken together, our study reveals dynamic regulatory roles played by neurogranin on synaptic plasticity, which provide mechanistic explanations for opposing experimental findings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that their employments to aSciStance Ltd and Scipio bioscience do not bring any competing interest to the findings in this publication. The authors also declare that there is no competing interest associated with their employment, any consultancy they may have carried out, any patents they may hold, any products in development or marketed products they have been involved in, etc.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Interactions between calmodulin and neurogranin govern the dynamics of CaMKII as a leaky integrator.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Jul 17;16(7):e1008015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008015. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32678848 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the neurogranin concentrated in spines in the induction of long-term potentiation.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 12;26(28):7337-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0729-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16837580 Free PMC article.
-
A Modeling and Analysis Study Reveals That CaMKII in Synaptic Plasticity Is a Dominant Affecter in CaM Systems in a T286 Phosphorylation-Dependent Manner.Molecules. 2022 Sep 14;27(18):5974. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185974. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144710 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII regulates the depalmitoylation and synaptic removal of the scaffold protein AKAP79/150 to mediate structural long-term depression.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 2;293(5):1551-1567. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.813808. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29196604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaMKII: a molecular substrate for synaptic plasticity and memory.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;122:61-87. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420170-5.00003-9. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014. PMID: 24484698 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporospatial expression of neurogranin in the rat molar development.J Mol Histol. 2025 Mar 29;56(2):123. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10401-x. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40156717
-
Calmodulin Binding Proteins and Alzheimer's Disease: Biomarkers, Regulatory Enzymes and Receptors That Are Regulated by Calmodulin.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 5;21(19):7344. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197344. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33027906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cooperation of Neurogranin with Calmodulin Promotes the Treatment of Aging-Related Diseases via Regular Exercise.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 26. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04959-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40285939 Review.
-
The effects of neurogranin knockdown on SERCA pump efficiency in soleus muscles of female mice fed a high fat diet.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 22;13:957182. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.957182. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36072929 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Synaptic and Axonal Dysfunction Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on CSF and Bioinformatic Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 17;23(18):10867. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810867. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhoads AR, Friedberg F. Sequence motifs for calmodulin recognition. The FASEB journal. 1997;11(5):331–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

