TNFα-mediated activation of NF-κB downregulates sodium-iodide symporter expression in thyroid cells
- PMID: 32049985
- PMCID: PMC7015378
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228794
TNFα-mediated activation of NF-κB downregulates sodium-iodide symporter expression in thyroid cells
Abstract
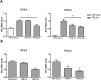
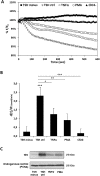
The sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) mediates transport of iodide across the basolateral membrane of thyroid cells. NIS expression in thyroid cancer (TC) cells allows the use of radioactive iodine (RAI) as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool, being RAI therapy the systemic treatment of choice for metastatic disease. Still, a significant proportion of patients with advanced TC lose the ability to respond to RAI therapy and no effective alternative therapies are available. Defective NIS expression is the main reason for impaired iodide uptake in TC and NIS downregulation has been associated with several pathways linked to malignant transformation. NF-κB signaling is one of the pathways associated with TC. Interestingly, NIS expression can be negatively regulated by TNF-α, a bona fide activator of NF-κB with a central role in thyroid autoimmunity. This prompted us to clarify NF-kB's role in this process. We confirmed that TNF-α leads to downregulation of TSH-induced NIS expression in non-neoplastic thyroid follicular cell-derived models. Notably, a similar effect was observed when NF-κB activation was triggered independently of ligand-receptor specificity, using phorbol-myristate-acetate (PMA). TNF-α and PMA downregulation of NIS expression was reverted when NF-κB-dependent transcription was blocked, demonstrating the requirement for NF-kB activity. Additionally, TNF-α and PMA were shown to have a negative impact on TSH-induced iodide uptake, consistent with the observed transcriptional downregulation of NIS. Our data support the involvement of NF-κB-directed transcription in the modulation of NIS expression, where up- or down-regulation of NIS depends on the combined output to NF-κB of several converging pathways. A better understanding of the mechanisms underlying NIS expression in the context of normal thyroid physiology may guide the development of pharmacological strategies to increase the efficiency of iodide uptake. Such strategies would be extremely useful in improving the response to RAI therapy in refractory-TC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of radioactive iodine refractoriness in differentiated thyroid cancer: Impaired sodium iodide symporter (NIS) expression owing to altered signaling pathway activity and intracellular localization of NIS.Theranostics. 2021 Apr 15;11(13):6251-6277. doi: 10.7150/thno.57689. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33995657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonistic effects of RAC1 and tumor-related RAC1b on NIS expression in thyroid.J Mol Endocrinol. 2019 Nov;63(4):309-320. doi: 10.1530/JME-19-0195. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31590142
-
MAPK Inhibition Requires Active RAC1 Signaling to Effectively Improve Iodide Uptake by Thyroid Follicular Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;13(22):5861. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225861. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34831012 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB p65 subunit mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced Na(+)/I(-) symporter gene expression by involving functional interaction with the paired domain transcription factor Pax8.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Sep;24(9):1846-62. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0102. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20667985 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of sodium/iodide symporter expression in thyroid and breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Sep;13(3):797-826. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01143. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16954431 Review.
Cited by
-
Transplantable human thyroid organoids generated from embryonic stem cells to rescue hypothyroidism.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 17;13(1):7057. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34776-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36396935 Free PMC article.
-
High Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 Expression Associated with Favorable Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.Endocr Pathol. 2024 Sep;35(3):245-255. doi: 10.1007/s12022-024-09815-2. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Endocr Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38884688
-
Potassium Iodide Induces Apoptosis in Salivary Gland Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5199. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115199. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508009 Free PMC article.
-
Salvianolic acid B inhibits RAW264.7 cell polarization towards the M1 phenotype by inhibiting NF-κB and Akt/mTOR pathway activation.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 16;12(1):13857. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18246-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35974091 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of radioactive iodine refractoriness in differentiated thyroid cancer: Impaired sodium iodide symporter (NIS) expression owing to altered signaling pathway activity and intracellular localization of NIS.Theranostics. 2021 Apr 15;11(13):6251-6277. doi: 10.7150/thno.57689. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33995657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dralle H, Machens A, Basa J, Fatourechi V, Franceschi S, Hay ID, et al. Follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2015;1: 15077. - PubMed
-
- Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, et al. Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid Off J Am Thyroid Assoc. 2006;16: 109–142. - PubMed
-
- Durante C, Haddy N, Baudin E, Leboulleux S, Hartl D, Travagli JP, et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91: 2892–2899. 10.1210/jc.2005-2838 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

