Human Fall Detection Based on Body Posture Spatio-Temporal Evolution
- PMID: 32050727
- PMCID: PMC7039221
- DOI: 10.3390/s20030946
Human Fall Detection Based on Body Posture Spatio-Temporal Evolution
Abstract
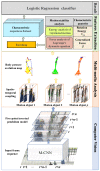
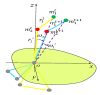
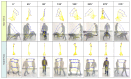
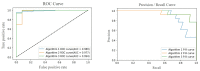
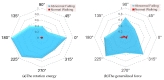
Abnormal falls in public places have significant safety hazards and can easily lead to serious consequences, such as trampling by people. Vision-driven fall event detection has the huge advantage of being non-invasive. However, in actual scenes, the fall behavior is rich in diversity, resulting in strong instability in detection. Based on the study of the stability of human body dynamics, the article proposes a new model of human posture representation of fall behavior, called the "five-point inverted pendulum model", and uses an improved two-branch multi-stage convolutional neural network (M-CNN) to extract and construct the inverted pendulum structure of human posture in real-world complex scenes. Furthermore, we consider the continuity of the fall event in time series, use multimedia analytics to observe the time series changes of human inverted pendulum structure, and construct a spatio-temporal evolution map of human posture movement. Finally, based on the integrated results of computer vision and multimedia analytics, we reveal the visual characteristics of the spatio-temporal evolution of human posture under the potentially unstable state, and explore two key features of human fall behavior: motion rotational energy and generalized force of motion. The experimental results in actual scenes show that the method has strong robustness, wide universality, and high detection accuracy.
Keywords: computer vision; fall behavior detection; five-point inverted pendulum model; human posture spatio-temporal map; motion instability; rotational energy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Yan S., Xiong Y., Lin D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition; Proceedings of theThirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence; New Orleans, LA, USA. 2–7 February 2017.
-
- Zhe C., Tomas S., Shih-En W., Yaser S. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields; Proceedings of the Conference of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); Honolulu, HI, USA. 21–26 July 2017.
-
- Sharma S., Kiros R., Salakhutdinov R. Action recognition using visual attention; Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Times Series Workshop; Montreal, QC, Canada. 7–12 December 2015; pp. 1–11.
-
- Gul V., Ivan L., Cordelia S. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017;40:1510–1517. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

