The biology of ergothioneine, an antioxidant nutraceutical
- PMID: 32051057
- PMCID: PMC7653990
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954422419000301
The biology of ergothioneine, an antioxidant nutraceutical
Abstract
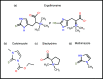
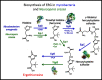
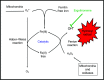
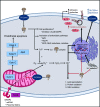
Ergothioneine (ERG) is an unusual thio-histidine betaine amino acid that has potent antioxidant activities. It is synthesised by a variety of microbes, especially fungi (including in mushroom fruiting bodies) and actinobacteria, but is not synthesised by plants and animals who acquire it via the soil and their diet, respectively. Animals have evolved a highly selective transporter for it, known as solute carrier family 22, member 4 (SLC22A4) in humans, signifying its importance, and ERG may even have the status of a vitamin. ERG accumulates differentially in various tissues, according to their expression of SLC22A4, favouring those such as erythrocytes that may be subject to oxidative stress. Mushroom or ERG consumption seems to provide significant prevention against oxidative stress in a large variety of systems. ERG seems to have strong cytoprotective status, and its concentration is lowered in a number of chronic inflammatory diseases. It has been passed as safe by regulatory agencies, and may have value as a nutraceutical and antioxidant more generally.
Keywords: Cytoprotectants; Ergothioneine; Nutraceuticals; Oxidative stress; SLC22A4.
Figures



References
-
- Kraemer K, Semba RD, Eggersdorfer M, et al. (2012) Introduction: the diverse and essential biological functions of vitamins. Ann Nutr Metab 61, 185–191. - PubMed
-
- Semba RD (2012) The discovery of the vitamins. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 82, 310–315. - PubMed
-
- Cheah IK & Halliwell B (2012) Ergothioneine; antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822, 784–793. - PubMed
-
- Halliwell B, Cheah IK & Drum CL (2016) Ergothioneine, an adaptive antioxidant for the protection of injured tissues? A hypothesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 470, 245–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

