Statin-induced GGPP depletion blocks macropinocytosis and starves cells with oncogenic defects
- PMID: 32051246
- PMCID: PMC7049144
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1917938117
Statin-induced GGPP depletion blocks macropinocytosis and starves cells with oncogenic defects
Erratum in
-
Correction for Jiao et al., Statin-induced GGPP depletion blocks macropinocytosis and starves cells with oncogenic defects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 23;117(25):14612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009107117. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32513707 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
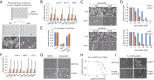
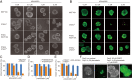
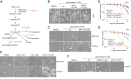
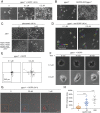
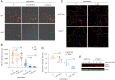
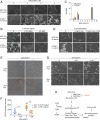
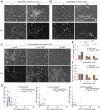
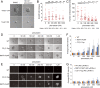
Cancer cells display novel characteristics which can be exploited for therapeutic advantage. Isolated studies have shown that 1) the mevalonate pathway and 2) increased macropinocytosis are important in tumorigenesis, but a connection between these two observations has not been envisioned. A library screen for compounds that selectively killed Dictyostelium pten- cells identified pitavastatin. Pitavastatin also killed human breast epithelial MCF10A cells lacking PTEN or expressing K-RasG12V, as well as mouse tumor organoids. The selective killing of cells with oncogenic defects was traced to GGPP (geranylgeranyl diphosphate) depletion. Disruption of GGPP synthase in Dictyostelium revealed that GGPP is needed for pseudopod extension and macropinocytosis. Fluid-phase uptake through macropinocytosis is lower in PTEN-deleted cells and, as reported previously, higher in cells expressing activated Ras. Nevertheless, uptake was more sensitive to pitavastatin in cells with either of these oncogenic mutations than in wild-type cells. Loading the residual macropinosomes after pitavastatin with high concentrations of protein mitigated the cell death, indicating that defective macropinocytosis leads to amino acid starvation. Our studies suggest that the dependence of cancer cells on the mevalonate pathway is due to the role of GGPP in macropinocytosis and the reliance of these cells on macropinocytosis for nutrient uptake. Thus, inhibition of the networks mediating these processes is likely to be effective in cancer intervention.
Keywords: cancer; chemotaxis; mevalonate pathway; small GTPases; tumor organoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

