SNAP23 depletion enables more SNAP25/calcium channel excitosome formation to increase insulin exocytosis in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 32051343
- PMCID: PMC7098801
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.129694
SNAP23 depletion enables more SNAP25/calcium channel excitosome formation to increase insulin exocytosis in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
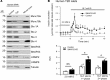
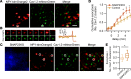
SNAP23 is the ubiquitous SNAP25 isoform that mediates secretion in non-neuronal cells, similar to SNAP25 in neurons. However, some secretory cells like pancreatic islet β cells contain an abundance of both SNAP25 and SNAP23, where SNAP23 is believed to play a redundant role to SNAP25. We show that SNAP23, when depleted in mouse β cells in vivo and human β cells (normal and type 2 diabetes [T2D] patients) in vitro, paradoxically increased biphasic glucose-stimulated insulin secretion corresponding to increased exocytosis of predocked and newcomer insulin granules. Such effects on T2D Goto-Kakizaki rats improved glucose homeostasis that was superior to conventional treatment with sulfonylurea glybenclamide. SNAP23, although fusion competent in slower secretory cells, in the context of β cells acts as a weak partial fusion agonist or inhibitory SNARE. Here, SNAP23 depletion promotes SNAP25 to bind calcium channels more quickly and longer where granule fusion occurs to increase exocytosis efficiency. β Cell SNAP23 antagonism is a strategy to treat diabetes.
Keywords: Beta cells; Diabetes; Endocrinology; Insulin; Metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

