A Protein Epitope Targeted by the Antibody Response to Kawasaki Disease
- PMID: 32052021
- PMCID: PMC7296860
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa066
A Protein Epitope Targeted by the Antibody Response to Kawasaki Disease
Abstract
Background: Kawasaki disease (KD) is the leading cause of childhood acquired heart disease in developed nations and can result in coronary artery aneurysms and death. Clinical and epidemiologic features implicate an infectious cause but specific antigenic targets of the disease are unknown. Peripheral blood plasmablasts are normally highly clonally diverse but the antibodies they encode are approximately 70% antigen-specific 1-2 weeks after infection.
Methods: We isolated single peripheral blood plasmablasts from children with KD 1-3 weeks after onset and prepared 60 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). We used the mAbs to identify their target antigens and assessed serologic response among KD patients and controls to specific antigen.
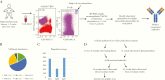
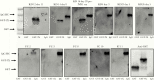
Results: Thirty-two mAbs from 9 of 11 patients recognize antigen within intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies in ciliated bronchial epithelial cells of fatal cases. Five of these mAbs, from 3 patients with coronary aneurysms, recognize a specific peptide, which blocks binding to inclusion bodies. Sera from 5/8 KD patients day ≥ 8 after illness onset, compared with 0/17 infant controls (P < .01), recognized the KD peptide antigen.
Conclusions: These results identify a protein epitope targeted by the antibody response to KD and provide a means to elucidate the pathogenesis of this important worldwide pediatric problem.
Keywords: Kawasaki disease; monoclonal antibodies; plasmablast.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Yanagawa H, Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, et al. . A nationwide incidence survey of Kawasaki disease in 1985–1986 in Japan. J Infect Dis 1988; 158:1296–301. - PubMed
-
- Yanagawa H, Nakamura Y, Kawasaki T, Shigematsu I. Nationwide epidemic of Kawasaki disease in Japan during winter of 1985-86. Lancet 1986; 2:1138–9. - PubMed
-
- McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, et al. ; American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017; 135:e927–99. - PubMed
-
- Makino N, Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, et al. . Epidemiological observations of Kawasaki disease in Japan, 2013–2014. Pediatr Int 2018; 60:581–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

