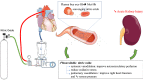
Is nitric oxide the forgotten nephroprotective treatment during cardiac surgery?
- PMID: 32052208
- PMCID: PMC7016086
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-020-0631-7
Is nitric oxide the forgotten nephroprotective treatment during cardiac surgery?
Conflict of interest statement
ML received research funding from the French ministry of health, research support from Sphingotec, lecture fees from Fresenius and Baxter and consulting fees from Novartis. The other authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of inhaled nitric oxide and milrinone for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension in adult cardiac surgery patients.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2000 Feb;14(1):12-7. doi: 10.1016/s1053-0770(00)90048-x. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2000. PMID: 10698385 Clinical Trial.
-
Response to nitric oxide during adult cardiac surgery.J Invest Surg. 2002 Jan-Feb;15(1):5-14. doi: 10.1080/08941930252807732. J Invest Surg. 2002. PMID: 11931495
-
Postoperative Inhaled Nitric Oxide Does Not Decrease Length of Stay in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Admissions.Pediatr Cardiol. 2019 Dec;40(8):1559-1568. doi: 10.1007/s00246-019-02187-z. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Pediatr Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31446473
-
Nitric Oxide in Cardiac Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018 Dec;32(6):2512-2519. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018. PMID: 29703580 Review.
-
Vascular changes after cardiopulmonary bypass and ischemic cardiac arrest: roles of nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999 Nov;32(11):1345-52. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1999001100004. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999. PMID: 10559835 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute kidney injury in patients with burns.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Mar;20(3):188-200. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00769-y. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37758939 Review.
-
Future insights of pharmacological prevention for AKI post cardiopulmonary bypass surgery (based on PK/PD approach).Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 22;13:975641. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.975641. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36210841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Yin and Yang of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Acute Kidney Injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 May 1;203(9):1053-1055. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4419ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33357099 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vermeulen Windsant IC, de Wit NCJ, Sertorio JTC, van Bijnen AA, Ganushchak YM, Heijmans JH, et al. Hemolysis during cardiac surgery is associated with increased intravascular nitric oxide consumption and perioperative kidney and intestinal tissue damage. Front Physiol. 2014;5:340. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00340. - DOI - PMC - PubMed