Estimation of genetic parameters and trends for production traits of dairy cattle in Thailand using a multiple-trait multiple-lactation test day model
- PMID: 32054206
- PMCID: PMC7468173
- DOI: 10.5713/ajas.19.0141
Estimation of genetic parameters and trends for production traits of dairy cattle in Thailand using a multiple-trait multiple-lactation test day model
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to estimate the genetic parameters and trends for milk, fat, and protein yields in the first three lactations of Thai dairy cattle using a 3-trait,- 3-lactation random regression test-day model.
Methods: Data included 168,996, 63,388, and 27,145 test-day records from the first, second, and third lactations, respectively. Records were from 19,068 cows calving from 1993 to 2013 in 124 herds. (Co) variance components were estimated by Bayesian methods. Gibbs sampling was used to obtain posterior distributions. The model included herd-year-month of testing, breed group-season of calving-month in tested milk group, linear and quadratic age at calving as fixed effects, and random regression coefficients for additive genetic and permanent environmental effects, which were defined as modified constant, linear, quadratic, cubic and quartic Legendre coefficients.
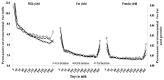
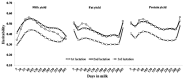
Results: Average daily heritabilities ranged from 0.36 to 0.48 for milk, 0.33 to 0.44 for fat and 0.37 to 0.48 for protein yields; they were higher in the third lactation for all traits. Heritabilities of test-day milk and protein yields for selected days in milk were higher in the middle than at the beginning or end of lactation, whereas those for test-day fat yields were high at the beginning and end of lactation. Genetics correlations (305-d yield) among production yields within lactations (0.44 to 0.69) were higher than those across lactations (0.36 to 0.68). The largest genetic correlation was observed between the first and second lactation. The genetic trends of 305-d milk, fat and protein yields were 230 to 250, 25 to 29, and 30 to 35 kg per year, respectively.
Conclusion: A random regression model seems to be a flexible and reliable procedure for the genetic evaluation of production yields. It can be used to perform breeding value estimation for national genetic evaluation in the Thai dairy cattle population.
Keywords: Genetic Parameter; Multiple-lactation; Multiple-traits; Random Regression Model; Thai Dairy Cattle.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genetic parameters for tunisian holsteins using a test-day random regression model.J Dairy Sci. 2008 May;91(5):2118-26. doi: 10.3168/jds.2007-0382. J Dairy Sci. 2008. PMID: 18420643
-
Genetic analysis of milk production traits of polish black and white cattle using large-scale random regression test-day models.J Dairy Sci. 2006 Aug;89(8):3152-63. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72589-9. J Dairy Sci. 2006. PMID: 16840632
-
Genetic parameters for test-day milk yield, lactation persistency, and fertility in low-, medium-, and high-production systems in Kenya.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Nov;103(11):10399-10413. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18350. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32921460
-
Experience with a test-day model.J Dairy Sci. 2000 May;83(5):1135-44. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(00)74979-4. J Dairy Sci. 2000. PMID: 10821590 Review.
-
Updating test-day milk yield factors for use in genetic evaluations and dairy production systems: a comprehensive review.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 11;14:1298114. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1298114. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38148978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Heat Stress on Milk Yield, Milk Fat-to-Protein Ratio, and Conception Rate in Thai-Holstein Dairy Cattle: A Phenotypic and Genetic Perspective.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;14(20):3026. doi: 10.3390/ani14203026. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457956 Free PMC article.
-
Determining Heat Stress Effects of Multiple Genetic Traits in Tropical Dairy Cattle Using Single-Step Genomic BLUP.Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 3;9(2):66. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9020066. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35202319 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic parameter estimates for daily predicted gross feed efficiency and its association with energy-corrected milk in South African Holstein cattle.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023 Sep 28;55(5):339. doi: 10.1007/s11250-023-03741-x. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023. PMID: 37770720 Free PMC article.
-
An Appropriate Genetic Approach for Improving Reproductive Traits in Crossbred Thai-Holstein Cattle under Heat Stress Conditions.Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 28;9(4):163. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9040163. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35448661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial Risk Distribution of Lumpy Skin Disease in Thailand Based on Maximum-Entropy Modeling.Animals (Basel). 2025 Aug 21;15(16):2456. doi: 10.3390/ani15162456. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Annual Information Dairy Cows [Internet] Department of Livestock Development; 2018. [cited 2019 Jan 15]. Available from: http://ict.dld.go.th/webnew/images/stories/stat_web/yearly/2561/land/T3-... (In Thai)
-
- Rekaya R, Carabano MJ, Toro MA. Use of test day yields for the genetic evaluation of production traits in Holstein-Friesian cattle. Livest Prod Sci. 1999;57:203–17. doi: 10.1016/S0301-6226(98)00181-X. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

