Loneliness and social isolation interventions for older adults: a scoping review of reviews
- PMID: 32054474
- PMCID: PMC7020371
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-8251-6
Loneliness and social isolation interventions for older adults: a scoping review of reviews
Abstract
Background: Loneliness and social isolation are growing public health concerns in our ageing society. Whilst these experiences occur across the life span, 50% of individuals aged over 60 are at risk of social isolation and one-third will experience some degree of loneliness later in life. The aim of this scoping review was to describe the range of interventions to reduce loneliness and social isolation among older adults that have been evaluated; in terms of intervention conceptualisation, categorisation, and components.
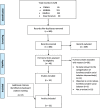
Methods: Three electronic databases (CINAHL, Embase and Medline) were systematically searched for relevant published reviews of interventions for loneliness and social isolation. Inclusion criteria were: review of any type, published in English, a target population of older people and reported data on the categorisation of loneliness and/or social isolation interventions. Data extracted included: categories of interventions and the reasoning underpinning this categorisation. The methodology framework proposed by Arskey and O'Malley and further developed by Levac, et al. was used to guide the scoping review process.
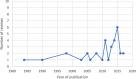
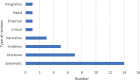
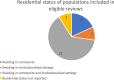
Results: A total of 33 reviews met the inclusion criteria, evaluating a range of interventions targeted at older people residing in the community or institutionalised settings. Authors of reviews included in this paper often used the same terms to categorise different intervention components and many did not provide a clear definition of these terms. There were inconsistent meanings attributed to intervention characteristics. Overall, interventions were commonly categorised on the basis of: 1) group or one-to-one delivery mode, 2) the goal of the intervention, and 3) the intervention type. Several authors replicated the categorisation system used in previous reviews.
Conclusion: Many interventions have been developed to combat loneliness and social isolation among older people. The individuality of the experience of loneliness and isolation may cause difficulty in the delivery of standardised interventions. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to addressing loneliness or social isolation, and hence the need to tailor interventions to suit the needs of individuals, specific groups or the degree of loneliness experienced. Therefore, future research should be aimed at discerning what intervention works for whom, in what particular context and how.
Keywords: Aged - ageing population - scoping; Loneliness; Lonely - Social isolation - socially isolated - older adults; Scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Campaign to End Loneliness . Loneliness is an international issue. 2013.
-
- Luanaigh CÓ, Lawlor BA. Loneliness and the health of older people. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008;23(12):1213–1221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

