Serum miRNAs are differentially altered by ethanol and caffeine consumption in rats
- PMID: 32055392
- PMCID: PMC7003974
- DOI: 10.1039/c9tx00069k
Serum miRNAs are differentially altered by ethanol and caffeine consumption in rats
Abstract
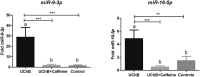
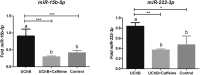
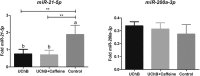
Alcoholism is a multifactorial disease with high risk for dependence determined by genetic background, environmental factors and neuroadaptations. The excessive consumption of this substance is related to psychiatric problems, epilepsy, cardiovascular disease, cirrhosis and cancers. Caffeine is one of the most popular psychostimulants currently consumed in the world. The combination of ethanol and caffeine ingested by consuming "energy drinks" is becoming increasingly popular among young people. We analyzed the effect of simultaneous consumption of ethanol and caffeine on the serum profile of miRNAs differentially expressed in the ethanol-drinking rat model (UChB strain). Adult rats were divided into three groups (n = 5 per group): UChB group (rats fed with 1 : 10 (v/v) ethanol ad libitum); UChB + caffeine group (rats fed with 1 : 10 (v/v) ethanol ad libitum + 3 g L-1 of caffeine); control group (rats drinking water used as the control for UChB). The treatment with caffeine occurred from day 95 to 150 days old, totalizing 55 days of ethanol + caffeine ingestion. The expressions of microRNAs (miR) -9-3p, -15b-5p, -16-5p, -21-5p, -200a-3p and -222-3p were detected by Real Time-PCR (RT-PCR). The expressions of miR-9-3p, -15b-5p, -16-5p and -222-3p were upregulated in the UChB group. Conversely, simultaneous ingestion of ethanol and caffeine significantly reversed these expressions to similar levels to control animals, thus emphasizing that caffeine had a protective effect in the presence of ethanol. In addition, miR-21-5p was downregulated with ethanol consumption whereas miR-222-3p was unchanged. Ethanol and caffeine consumption was capable of altering serum miRNAs, which are potential biomarkers for the systemic effects of these addictive substances.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caffeine consumption attenuates ethanol-induced inflammation through the regulation of adenosinergic receptors in the UChB rats cerebellum.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 Jul 24;10(4):835-849. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab067. eCollection 2021 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34484675 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol and caffeine consumption modulates the expression of miRNAs in the cerebellum and plasma of UChB rats.Life Sci. 2019 Jul 15;229:180-186. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.016. Epub 2019 May 8. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31077720
-
Interactions of ethanol and caffeine on apoptosis in the rat cerebellum (voluntary ethanol consumers).Cell Biol Int. 2018 Nov;42(11):1575-1583. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11054. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 30203895
-
The UChA and UChB rat lines: metabolic and genetic differences influencing ethanol intake.Addict Biol. 2006 Sep;11(3-4):310-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2006.00030.x. Addict Biol. 2006. PMID: 16961761 Review.
-
Systematic Review and Bioinformatic Analysis of microRNA Expression in Autism Spectrum Disorder Identifies Pathways Associated With Cancer, Metabolism, Cell Signaling, and Cell Adhesion.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Oct 21;12:630876. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.630876. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34744804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Epigenetic Effects of Coffee.Molecules. 2023 Feb 13;28(4):1770. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041770. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional roles, regulatory mechanisms and theranostics applications of ncRNAs in alcohol use disorder.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;19(4):1316-1335. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.81518. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36923934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Biomarker Panel of Radiation-Upregulated miRNA as Signature for Ionizing Radiation Exposure.Life (Basel). 2020 Dec 18;10(12):361. doi: 10.3390/life10120361. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33352926 Free PMC article.
-
miR-9 utilizes precursor pathways in adaptation to alcohol in mouse striatal neurons.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2023;3:11323. doi: 10.3389/adar.2023.11323. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2023. PMID: 38116240 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine consumption attenuates ethanol-induced inflammation through the regulation of adenosinergic receptors in the UChB rats cerebellum.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 Jul 24;10(4):835-849. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab067. eCollection 2021 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34484675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO, World Health Organization, Global status report on alcohol and health, Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
-
- Beresford T. P., Wongngamnit N. and Temple B. A., Alcoholism: diagnosis, prognosis, epidemiology, and burden of the disease, in Handbooks of Neurology, 2014, vol. 125, pp. 3–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

