Semiconductor Quantum Dots as Components of Photoactive Supramolecular Architectures
- PMID: 32055433
- PMCID: PMC7008307
- DOI: 10.1002/open.201900336
Semiconductor Quantum Dots as Components of Photoactive Supramolecular Architectures
Abstract
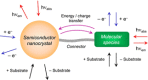
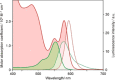
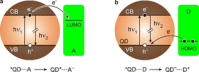
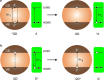
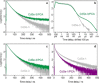
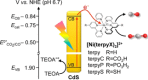
Luminescent quantum dots (QDs) are colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals consisting of an inorganic core covered by a molecular layer of organic surfactants. Although QDs have been known for more than thirty years, they are still attracting the interest of researchers because of their unique size-tunable optical and electrical properties arising from quantum confinement. Moreover, the controlled decoration of the QD surface with suitable molecular species enables the rational design of inorganic-organic multicomponent architectures that can show a vast array of functionalities. This minireview highlights the recent progress in the use of surface-modified QDs - in particular, those based on cadmium chalcogenides - as supramolecular platforms for light-related applications such as optical sensing, triplet photosensitization, photocatalysis and phototherapy.
Keywords: catalysis; quantum dots; sensing; supramolecular chemistry; triplet sensitization.
©2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures










References
-
- Alivisatos A. P., J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 13226–13239.
-
- Resch-Genger U., Grabolle M., Cavaliere-Jaricot S., Nitschke R., Nann T., Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. - PubMed
-
- Ekimov A. I., Efros Al. L., Onushchenko A. A., Solid State Commun. 1985, 56, 921–924.
-
- Brus L. E., J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 4403–4409.
-
- See, e. g.: Murray C. B., Norris D. J., Bawendi M. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706–8715.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

