Emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by candida species: A case report and outcome of 1 year follow-up
- PMID: 32055447
- PMCID: PMC7005417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eucr.2020.101113
Emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by candida species: A case report and outcome of 1 year follow-up
Abstract
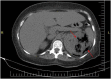
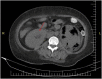
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is an acute life-threatening gas-forming necrotizing infection of the renal parenchyma and its surrounding tissues. EPN requires early diagnosis and management because of related life-threatening septic complications. Gram-negative bacteria remain the most common causative organisms. Although candida species as a causative pathogen in emphysematous pyelonephritis is very rare, we report a rare case of emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by candida species successfully managed with unilateral nephrectomy and outcome for flow up in one year.
Keywords: Diabetes; Emphysematous pyelonephritis; Nephrectomy.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Singh Ubee Sarvpreet, McGlynn Laura, Fordham Mark. Emphysematous pyelonephritis. BJU International ©. 2010;107:1474–1478. BJU International. - PubMed
-
- Huang Jeng-Jong, Tseng Chin-Chung. Emphysematous Pyelonephritis clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(6):797–805. - PubMed
-
- Matthew E., Falagas Risk factors for mortality in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis: a meta-analysis. J Urol. September 2007;178:880–885. - PubMed
-
- Khaira Ambar. Retrospective analysis of clinical profile prognostic factors and outcomes of 19 patients of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2009;41:959–966. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources