A review of computational drug repurposing
- PMID: 32055582
- PMCID: PMC6989243
- DOI: 10.12793/tcp.2019.27.2.59
A review of computational drug repurposing
Abstract
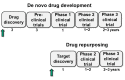
Although sciences and technology have progressed rapidly, de novo drug development has been a costly and time-consuming process over the past decades. In view of these circumstances, 'drug repurposing' (or 'drug repositioning') has appeared as an alternative tool to accelerate drug development process by seeking new indications for already approved drugs rather than discovering de novo drug compounds, nowadays accounting for 30% of newly marked drugs in the U.S. In the meantime, the explosive and large-scale growth of molecular, genomic and phenotypic data of pharmacological compounds is enabling the development of new area of drug repurposing called computational drug repurposing. This review provides an overview of recent progress in the area of computational drug repurposing. First, it summarizes available repositioning strategies, followed by computational methods commonly used. Then, it describes validation techniques for repurposing studies. Finally, it concludes by discussing the remaining challenges in computational repurposing.
Keywords: Computational drug repurposing; Deep learning; Drug repositioning; Machine learning; Text mining.
Copyright © 2019 Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: - Authors: The author declared no conflict of interest. - Reviewers: Nothing to declare - Editors: Nothing to declare
Figures
References
-
- Booth B, Zemmel R. Opinion/Outlook: Prospects for productivity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:451–456. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
