Cognitive function and its relationship with brain structure in myotonic dystrophy type 1
- PMID: 32056295
- PMCID: PMC7872331
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.24595
Cognitive function and its relationship with brain structure in myotonic dystrophy type 1
Abstract
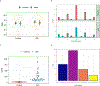
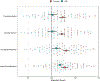
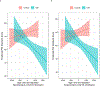
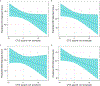
Studies have shown relationships between white matter abnormalities and cognitive dysfunction in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), but comprehensive analysis of potential structure-function relationships are lacking. Fifty adult-onset DM1 individuals (33 female) and 68 unaffected adults (45 female) completed the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV (WAIS-IV) to determine the levels and patterns of intellectual functioning. Neuroimages were acquired with a 3T scanner and were processed with BrainsTools. Regional brain volumes (regions of interest, ROIs) were adjusted for inter-scanner variation and intracranial volume. Linear regression models were conducted to assess if group by ROI interaction terms significantly predicted WAIS-IV composite scores. Models were adjusted for age and sex. The DM1 group had lower Perceptual Reasoning Index (PRI), Working Memory Index (WMI), and Processing Speed Index (PSI) scores than the unaffected group (PRI t(113) = -3.28, p = 0.0014; WMI t(114) = -3.49, p = 0.0007; PSI t(114) = -2.98, p = 0.0035). The group by hippocampus interaction term was significant for both PRI and PSI (PRI (t(111) = -2.82, p = 0.0057; PSI (t(112) = -2.87, p = 0.0049)). There was an inverse association between hippocampal volume and both PRI and PSI in the DM1 group (the higher the volume, the lower the intelligence quotient scores), but no such association was observed in the unaffected group. Enlarged hippocampal volume may underlie some aspects of cognitive dysfunction in adult-onset DM1, suggesting that increased volume of the hippocampus may be pathological.
Keywords: DM1; WAIS-IV; cognitive impairments; hippocampus; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroanatomy.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
No authors have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest: None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Baldanzi S, Cecchi P, Fabbri S, Pesaresi I, Simoncini C, Angelini C, … Siciliano G (2016). Relationship between neuropsychological impairment and grey and white matter changes in adult-onset myotonic dystrophy type 1. NeuroImage: Clinical, 12, 190–197. 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.06.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Censori B, Danni M, Del Pesce M, & Provinciali L (1990). Neuropsychological profile in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol, 237(4), 251–256. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

