High levels of dd-cfDNA identify patients with TCMR 1A and borderline allograft rejection at elevated risk of graft injury
- PMID: 32056331
- PMCID: PMC7496411
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15822
High levels of dd-cfDNA identify patients with TCMR 1A and borderline allograft rejection at elevated risk of graft injury
Abstract
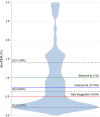
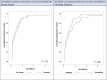
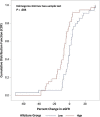
The clinical importance of subclinical, early T cell-mediated rejection (Banff TCMR 1A and borderline lesions) remains unclear, due, in part to the fact that histologic lesions used to characterize early TCMR can be nonspecific. Donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA) is an important molecular marker of active graft injury. Over a study period from June 2017 to May 2019, we assessed clinical outcomes in 79 patients diagnosed with TCMR 1A/borderline rejection across 11 US centers with a simultaneous measurement of dd-cfDNA. Forty-two patients had elevated dd-cfDNA (≥0.5%) and 37 patients had low levels (<0.5%). Elevated levels of dd-cfDNA predicted adverse clinical outcomes: among patients with elevated cfDNA, estimated glomerular filtration rate declined by 8.5% (interquartile rate [IQR] -16.22% to -1.39%) (-3.50 mL/min/1.73 m2 IQR -8.00 to -1.00) vs 0% (-4.92%, 4.76%) in low dd-cfDNA patients (P = .004), de novo donor-specific antibody formation was seen in 40% (17/42) vs 2.7% (P < .0001), and future or persistent rejection occurred in 9 of 42 patients (21.4%) vs 0% (P = .003). The use of dd-cfDNA may complement the Banff classification and to risk stratify patients with borderline/TCMR 1A identified on biopsy.
Keywords: biomarker; cellular transplantation (non-islet); clinical research/practice; kidney (allograft) function/dysfunction; kidney failure/injury; monitoring: immune; rejection: T cell mediated (TCMR).
© 2020 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Patients were tested with AlloSure dd‐cfDNA as part of standard care. No financial incentives were received for this project and it was done independently. There are no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Katsuma AI, Yamakawa T, Nakada Y, Yamamoto I, Yokoo T. Histopathological findings in transplanted kidneys. Ren Replace Ther. 2017;3:6.
-
- Nankivell BJ, Agrawal N, Sharma A, et al. The clinical and pathological significance of borderline T cell mediated rejection. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(5):1452‐1463. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

