Salivary biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32056455
- PMCID: PMC7877992
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1730431
Salivary biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis
Abstract
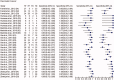
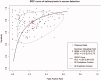
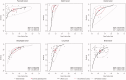
Background: Saliva represents a promising non-invasive source of novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis cancer. This meta-analysis evaluates the diagnostic value of salivary biomarkers for detection of malignant non-oral tumours to better define the value of saliva as an alternative liquid biopsy.Materials and methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis. PubMed, Embase, LILACS and the Cochrane Library were searched to identify articles that examined the potential of salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis of malignant non-oral tumours. To assess the overall accuracy, we calculated the diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), area under hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (AUC) curve, sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) using a random- or fixed-effects model. Heterogeneity and publication bias were assessed. Statistical tests were two-sided.Results: One hundred fifty-five study units from 29 articles with 11,153 subjects were included. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, DOR and AUC were 0.76 (95% confidence intervals (CI), 0.74-0.77), 0.76 (95% CI, 0.75-0.77), 3.22 (95% CI, 2.92-3.55), 0.31 (95% CI, 0.28-0.34), 13.42 (95% CI, 12.28-15.96) and 0.85 (95% CI, 0.84-0.87), respectively.Conclusion: Salivary biomarkers may be potentially used for non-invasive diagnosis of malignant non-oral tumours.Key messagesThis meta-analysis evaluates the diagnostic value of salivary biomarkers for detection of malignant non-oral tumours to better define the role of saliva as an alternative liquid biopsy.Salivary biomarkers showed 85% accuracy for cancer distant to the oral cavity.Saliva represents a promising non-invasive source of novel biomarkers in cancer.
Keywords: Saliva; cancer; diagnosis; liquid biopsy; meta-analysis; salivaomics; salivary biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
R.L.-L. reported Nasasbiotech during the conduct of the study; received grants and personal fees from Roche and Merck, personal fees from AstraZeneca, Pharmamar, Leo and Bayer and personal fees and non-financial support from BMS outside the submitted work. The rest of the authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures




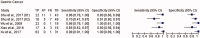
Comment in
-
Commentary on: Salivary biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2020 May-Jun;52(3-4):145. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1743351. Epub 2020 Mar 22. Ann Med. 2020. PMID: 32167392 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to commentary by Lu and Wang on "Salivary biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis".Ann Med. 2020 May-Jun;52(3-4):146. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1746391. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Ann Med. 2020. PMID: 32202950 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Schiffman JD, Fisher PG, Gibbs P. Early detection of cancer: past, present, and future. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2015:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Nair M, Sandhu SS, Sharma AK. Cancer molecular markers: a guide to cancer detection and management. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;52:39–55. - PubMed
-
- Crowley E, Di Nicolantonio F, Loupakis F, et al. Liquid biopsy: monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:472–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
