Toxicity of oil spill response agents and crude oils to five aquatic test species
- PMID: 32056858
- PMCID: PMC7425839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.110954
Toxicity of oil spill response agents and crude oils to five aquatic test species
Abstract
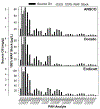
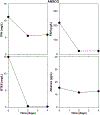
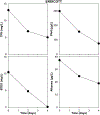
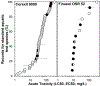
The majority of aquatic toxicity data for petroleum products has been limited to a few intensively studied crude oils and Corexit chemical dispersants, and acute toxicity testing in two standard estuarine test species: mysids (Americamysis bahia) and inland silversides (Menidia beryllina). This study compared the toxicity of two chemical dispersants commonly stock piled for spill response (Corexit EC9500A®, Finasol®OSR 52), three less studied agents (Accell Clean®DWD dispersant; CytoSol® surface washing agent; Gelco200® solidifier), and three crude oils differing in hydrocarbon composition (Dorado, Endicott, Alaska North Slope). Consistent with listings on the U.S. National Contingency Plan Product Schedule, general rank order toxicity was greatest for dispersants and lowest for the solidifier. The results indicate that freshwater species can have similar sensitivity as the conventionally tested mysids and silversides, and that the sea urchin (Arbacia punctulata) appears to be a reasonable addition to increase taxa diversity in standardized oil agent testing.
Keywords: Dispersant; Oil; Spill response; Toxicity.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Baker JM. 1995. Net environmental benefit analysis for oil spill response. International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings: February-March 1995, Vol. 1995, No. 1, pp. 611–614. 10.7901/2169-3358-1995-1-611 - DOI
-
- Barron MG Chiasson SC, Bejarano AC. 2019. Ecotoxicology of deep ocean spills In: Deep Oil Spills. Chapter 27, p. 466–479. Springer.
-
- Barron MG, Hemmer MJ, Jackson CR. 2013. Development of aquatic toxicity benchmarks for oil products using species sensitivity distributions. Integra Env Assess Manag 9, 610–615. - PubMed
-
- Barron MG, Lilavois CR, Martin TM. 2015. MOAtox: a comprehensive mode of action and acute aquatic toxicity database for predictive model development. Aquat Tox 16, 102–107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

