The selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic and anti-parkinsonian-like effects in MPTP-treated marmosets
- PMID: 32057799
- PMCID: PMC7103782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.107997
The selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic and anti-parkinsonian-like effects in MPTP-treated marmosets
Abstract
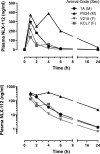
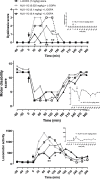
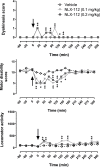
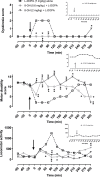
l-DOPA is the gold-standard pharmacotherapy for treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) but can lead to the appearance of troubling dyskinesia which are attributable to 'false neurotransmitter' release of dopamine by serotonergic neurons. Reducing the activity of these neurons diminishes l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (LID), but there are currently no clinically approved selective, high efficacy 5-HT1A receptor agonists. Here we describe the effects of NLX-112, a highly selective and efficacious 5-HT1A receptor agonist, on LID in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-treated marmosets, a non-human primate model of PD. NLX-112 exhibited modest plasma half-life (~2h) and marked plasma protein binding (96%). When administered to parkinsonian marmosets with l-DOPA (7 mg/kg p.o.), NLX-112 (0.025, 0.1 and 0.4 mg/kg p.o.) reduced LID scores at early time-points after administration, whilst only minimally interfering with the l-DOPA-induced reversal of motor disability. In contrast, the prototypical 5-HT1A receptor agonist, (+)8-OH-DPAT (0.6 and 2 mg/kg p. o.), reduced LID but also abolished l-DOPA's anti-disability activity. Administered by itself, NLX-112 (0.1, 0.2 mg/kg p.o.) produced very little dyskinesia or locomotor activity, but reduced motor disability scores by about half the extent elicited by l-DOPA, suggesting that it may have motor facilitation effects of its own. Both NLX-112 and (+)8-OH-DPAT induced unusual and dose-limiting behaviors in marmoset that resembled 'serotonin behavioral syndrome' observed previously in rat. Overall, the present study showed that NLX-112 has anti-LID activity at the doses tested as well as reducing motor disability. The data suggest that additional investigation of NLX-112 is desirable to explore its potential as a treatment for PD and PD-LID.
Keywords: Befiradol; MPTP; Marmosets; NLX-112; Parkinson's disease; Serotonin 5-HT(1A) receptors; l-DOPA-Induced dyskinesia.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest AN-T, MAV and RD are employees and/or stockholders of Neurolixis Inc. The other authors have no disclosures.
Figures
References
-
- Aubert Y., Gustison M.L., Gardner L.A., Bohl M.A., Lange J.R., Allers K.A., Sommer B., Datson N.A., Abbott D.H. Flibanserin and 8-OH-DPAT implicate serotonin in association between female marmoset monkey sexual behavior and changes in pair-bond quality. J. Sex. Med. 2012;9(3):694–707. PMID: 22304661. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardin L., Assie M.B., Pelissou M., Royer-Urios I., Newman-Tancredi A., Ribet J.P., Sautel F., Koek W., Colpaert F.C. Dual, hyperalgesic, and analgesic effects of the high-efficacy 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A (5-HT1A) agonist F 13640 [(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-[4-fluoro-4-{[(5-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-am ino]-methyl}piperidin-1-yl]methanone, fumaric acid salt]: relationship with 5-HT1A receptor occupancy and kinetic parameters. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therapeut. 2005;312(3):1034–1042. PMID: 15528450. - PubMed
-
- Bezard E., Tronci E., Pioli E.Y., Li Q., Porras G., Bjorklund A., Carta M. Study of the antidyskinetic effect of eltoprazine in animal models of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Movement disorders. Mov Disord. 2013;28(8):1088–1096. PMID: 23389842. - PubMed
-
- Brys I., Halje P., Scheffer-Teixeira R., Varney M., Newman-Tancredi A., Petersson P. Neurophysiological effects in cortico-basal ganglia-thalamic circuits of antidyskinetic treatment with 5-HT1A receptor biased agonists. Exp. Neurol. 2018;302:155–168. PMID: 29339052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

