The role of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex on the neuromuscular system
- PMID: 32057921
- PMCID: PMC8792866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134833
The role of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex on the neuromuscular system
Abstract
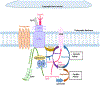
The Dystrophin Glycoprotein Complex (DGC) is a large multi-protein complex that links cytoskeleton actin to the extracellular matrix. This complex is critical in maintaining the structural integrity of muscle fibers and the stability of the neuromuscular synapse. The DGC consists of dystrophin and its utrophin homolog, as well as dystroglycans, sarcoglycans, sarcospan, syntrophins, and dystrobrevins. Deficiencies in DGC proteins result in several forms of muscular dystrophy with varying symptoms and degrees of severity in addition to structurally abnormal neuromuscular junctions (NMJs). This mini-review highlights current knowledge regarding the role of the DGC on the molecular dynamics of acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) as it relates to the formation and maintenance of the mammalian NMJ.
Keywords: AChR dynamics; Dystrophin glycoprotein complex; Neuromuscular junction.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Tintignac LA, Brenner HR, and Ruegg MA, Mechanisms Regulating Neuromuscular Junction Development and Function and Causes of Muscle Wasting. Physiol Rev, 2015. 95(3): p. 809–52. - PubMed
-
- Flucher BE and Daniels MP, Distribution of Na+ channels and ankyrin in neuromuscular junctions is complementary to that of acetylcholine receptors and the 43 kd protein. Neuron, 1989. 3(2): p. 163–75. - PubMed
-
- Fambrough DM, Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev, 1979. 59(1): p. 165–227. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, et al., DNA topoisomerase IIbeta and neural development. Science, 2000. 287(5450): p. 131–4. - PubMed
-
- Lin W, et al., Distinct roles of nerve and muscle in postsynaptic differentiation of the neuromuscular synapse. Nature, 2001. 410(6832): p. 1057–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

