Common innate pathways to autoimmune disease
- PMID: 32058071
- PMCID: PMC8324042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108361
Common innate pathways to autoimmune disease
Abstract
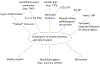
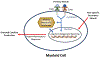
Until recently, autoimmune disease research has primarily been focused on elucidating the role of the adaptive immune system. In the past decade or so, the role of the innate immune system in the pathogenesis of autoimmunity has increasingly been realized. Recent findings have elucidated paradigm-shifting concepts, for example, the implications of "trained immunity" and a dysbiotic microbiome in the susceptibility of predisposed individuals to clinical autoimmunity. In addition, the application of modern technologies such as the quantum dot (Qdot) system and 'Omics' (e.g., genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) data-processing tools has proven fruitful in revisiting mechanisms underlying autoimmune pathogenesis and in identifying novel therapeutic targets. This review highlights recent findings discussed at the American Autoimmune Related Disease Association (AARDA) 2019 colloquium. The findings covering autoimmune diseases and autoinflammatory diseases illustrate how new developments in common innate immune pathways can contribute to the better understanding and management of these immune-mediated disorders.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; Autoimmunity; Autoinflammatory disease; Inflammation; Innate immunity; Trained immunity.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- AARDA, (American Autoimmune Related Disease Association) Autoimmune Disease Statistics, American Autoimmune Related Disease Association, (2018).
-
- Ermann J, Fathman CG, Autoimmune diseases: genes, bugs and failed regulation, Nat. Immunol 2 (2001) 759–761. - PubMed
-
- Carroll M, Innate immunity in the etiopathology of autoimmunity, Nat. Immunol 2 (2001) 1089–1090. - PubMed
-
- Rose NR, The adjuvant effect in infection and autoimmunity, Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol 34 (2008) 279–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

