The Functional Consequences of Eukaryotic Topoisomerase 1 Interaction with G-Quadruplex DNA
- PMID: 32059547
- PMCID: PMC7073998
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11020193
The Functional Consequences of Eukaryotic Topoisomerase 1 Interaction with G-Quadruplex DNA
Abstract
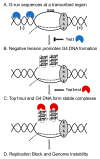
Topoisomerase I in eukaryotic cells is an important regulator of DNA topology. Its catalytic function is to remove positive or negative superhelical tension by binding to duplex DNA, creating a reversible single-strand break, and finally religating the broken strand. Proper maintenance of DNA topological homeostasis, in turn, is critically important in the regulation of replication, transcription, DNA repair, and other processes of DNA metabolism. One of the cellular processes regulated by the DNA topology and thus by Topoisomerase I is the formation of non-canonical DNA structures. Non-canonical or non-B DNA structures, including the four-stranded G-quadruplex or G4 DNA, are potentially pathological in that they interfere with replication or transcription, forming hotspots of genome instability. In this review, we first describe the role of Topoisomerase I in reducing the formation of non-canonical nucleic acid structures in the genome. We further discuss the interesting recent discovery that Top1 and Top1 mutants bind to G4 DNA structures in vivo and in vitro and speculate on the possible consequences of these interactions.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; genome instability; topoisomerase I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

