Persistent Polyfunctional Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells That Target Glypican 3 Eliminate Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Mice
- PMID: 32060001
- PMCID: PMC7282931
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.011
Persistent Polyfunctional Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells That Target Glypican 3 Eliminate Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Mice
Erratum in
-
Correction.Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1433. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.025. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 33606993 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and aims: Glypican 3 (GPC3) is an oncofetal antigen involved in Wnt-dependent cell proliferation that is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We investigated whether the functions of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that target GPC3 are affected by their antibody-binding properties.
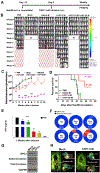
Methods: We collected peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors and patients with HCC and used them to create CAR T cells, based on the humanized YP7 (hYP7) and HN3 antibodies, which have high affinities for the C-lobe and N-lobe of GPC3, respectively. NOD/SCID/IL-2Rgcnull (NSG) mice were given intraperitoneal injections of luciferase-expressing (Luc) Hep3B or HepG2 cells and after xenograft tumors formed, mice were given injections of saline or untransduced T cells (mock control), or CAR (HN3) T cells or CAR (hYP7) T cells. In other NOD/SCID/IL-2Rgcnull (NSG) mice, HepG2-Luc or Hep3B-Luc cells were injected into liver, and after orthotopic tumors formed, mice were given 1 injection of CAR (hYP7) T cells or CD19 CAR T cells (control). We developed droplet digital polymerase chain reaction and genome sequencing methods to analyze persistent CAR T cells in mice.
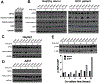
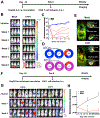
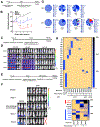
Results: Injections of CAR (hYP7) T cells eliminated tumors in 66% of mice by week 3, whereas CAR (HN3) T cells did not reduce tumor burden. Mice given CAR (hYP7) T cells remained tumor free after re-challenge with additional Hep3B cells. The CAR T cells induced perforin- and granzyme-mediated apoptosis and reduced levels of active β-catenin in HCC cells. Mice injected with CAR (hYP7) T cells had persistent expansion of T cells and subsets of polyfunctional CAR T cells via antigen-induced selection. These T cells were observed in the tumor microenvironment and spleen for up to 7 weeks after CAR T-cell administration. Integration sites in pre-infusion CAR (HN3) and CAR (hYP7) T cells were randomly distributed, whereas integration into NUPL1 was detected in 3.9% of CAR (hYP7) T cells 5 weeks after injection into tumor-bearing mice and 18.1% of CAR (hYP7) T cells at week 7. There was no common site of integration in CAR (HN3) or CD19 CAR T cells from tumor-bearing mice.
Conclusions: In mice with xenograft or orthoptic liver tumors, CAR (hYP7) T cells eliminate GPC3-positive HCC cells, possibly by inducing perforin- and granzyme-mediated apoptosis or reducing Wnt signaling in tumor cells. GPC3-targeted CAR T cells might be developed for treatment of patients with HCC.
Keywords: Hepatic; Immunotherapy; Lymphocyte; Tumor-Specific T Cells.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Hsu HC, Cheng W, Lai PL. Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated transcript MXR7 in hepatocellular carcinoma: biological significance and temporospatial distribution. Cancer Res 1997;57:5179–84. - PubMed
-
- Capurro M, Wanless IR, Sherman M, et al. Glypican-3: a novel serum and histochemical marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2003;125:89–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

