Introduction to Radiomics
- PMID: 32060219
- PMCID: PMC9374044
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.118.222893
Introduction to Radiomics
Abstract
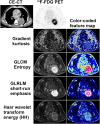
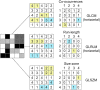
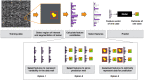
Radiomics is a rapidly evolving field of research concerned with the extraction of quantitative metrics-the so-called radiomic features-within medical images. Radiomic features capture tissue and lesion characteristics such as heterogeneity and shape and may, alone or in combination with demographic, histologic, genomic, or proteomic data, be used for clinical problem solving. The goal of this continuing education article is to provide an introduction to the field, covering the basic radiomics workflow: feature calculation and selection, dimensionality reduction, and data processing. Potential clinical applications in nuclear medicine that include PET radiomics-based prediction of treatment response and survival will be discussed. Current limitations of radiomics, such as sensitivity to acquisition parameter variations, and common pitfalls will also be covered.
Keywords: PET; artificial intelligence; machine learning; radiomics; single-photon emission tomography.
© 2020 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures
References
-
- Yang F, Wang Y, Li Q, et al. . Intratumor heterogeneity predicts metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2017;38:900–909. - PubMed
-
- Burrell RA, McGranahan N, Bartek J, Swanton C. The causes and consequences of genetic heterogeneity in cancer evolution. Nature. 2013;501:338–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
