A comparative study on the short-term clinical efficacy of the modified laparoscopic uterine comminution technique and traditional methods
- PMID: 32064100
- PMCID: PMC7016613
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2020.1982
A comparative study on the short-term clinical efficacy of the modified laparoscopic uterine comminution technique and traditional methods
Abstract
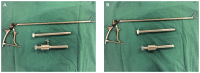
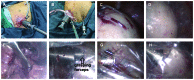
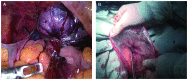
To assess the value of the modified laparoscopic uterine comminution technique in laparoscopic uterine surgery, a total of 82 cases of laparoscopic myomectomy were divided into the traditional group and modified group, according to a random number table. During the same period, 92 patients who underwent laparoscopic hysterectomy were divided into the conventional group and the modified group, according to a random number table. The patients in the conventional group and modified group who underwent laparoscopic uterine fibroid removal showed no significant differences in the operation time, blood loss or average hospitalization (P>0.05). There was no significant difference in the operative time or average length of hospital stay between patients in the conventional group and modified group who underwent laparoscopic hysterectomy (P>0.05). In laparoscopic myomectomy, the fibroid specimens were placed in a self-made specimen bag for modified uterine comminution. In laparoscopic hysterectomy, the whole uterus specimen was placed in a self-made specimen bag and viewed from the vagina. The improved comminution technique is simple and feasible, does not increase the operation time or length of hospitalization, and has value for clinical use.
Keywords: laparoscopic hysterectomy; laparoscopic myomectomy; modified laparoscopic uterine smashing technique.
Copyright: © Shi et al.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
