A comparative study of nivolumab and axitinib in terms of overall survival, treatment continuation, and cost for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32064108
- PMCID: PMC7016520
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2020.1978
A comparative study of nivolumab and axitinib in terms of overall survival, treatment continuation, and cost for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
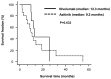
Nivolumab and axitinib has recommended as a second-line treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) after tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. In this study, overall survival (OS), treatment continuation, and the cost of nivolumab and axitinib-the second-line treatment agents for mRCC-were compared and examined. Herein, we retrospectively surveyed patients with pathologically confirmed mRCC, treated with nivolumab (n=9) or axitinib (n=16) at Ogaki Municipal Hospital (Ogaki, Japan) between January 2012 and May 2019. The treatment periods for the nivolumab- and axitinib-administered groups were 5.4 (range: 1.4-21.3) and 3.4 (range: 0.3-28.1) months, respectively (P=0.089). The postponement periods for the nivolumab- and axitinib-administered groups were 7 (range: 0-186) and 0 (range: 0-262) days, respectively, and the difference was statistically significant (P=0.008). The median OS for patients treated with nivolumab and axitinib was 12.3 (range: 1.5-25.5 months) and 9.2 (range: 2.2-55.0 months) months, respectively (P=0.633). The one-year cost estimates for axitinib and nivolumab in clinical practice were $60,694.2 and $86,544.4, respectively (P=0.017). We found that despite frequent interruptions in nivolumab administration and a longer postpaonement period for the nivolumab-administered group than for the axitinib-administered group, both groups exhibit comparable treatment duration and OS.
Keywords: advanced/recurrent renal cancer; axitinib; nivolumab; overall survival; second-line treatment.
Copyright © 2019, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative study on nivolumab and axitinib as secondary treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A multi-institutional retrospective study in Japan.Int J Urol. 2023 Sep;30(9):723-729. doi: 10.1111/iju.15130. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Int J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36578154
-
Comparison of second-line treatments in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients: A single-center experience.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13;102(41):e35245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035245. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37832108 Free PMC article.
-
Second-line targeted therapies after nivolumab-ipilimumab failure in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Feb;108:33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.11.031. Epub 2019 Jan 5. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30616146
-
Evaluating the safety and efficacy of axitinib in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2015 Feb 11;7:65-73. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S74202. eCollection 2015. Cancer Manag Res. 2015. PMID: 25709499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive overview of axitinib development in solid malignancies: focus on metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2012 May;10(5):307-14. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22706540 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Needing a Second-Line Therapy: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 4;12(12):3634. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123634. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33291600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Review.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Nov-Dec;47(6):1228-1242. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0681. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33650838 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang C, Thudium KB, Han M, Wang XT, Huang H, Feingersh D, Garcia C, Wu Y, Kuhne M, Srinivasan M, et al. In vitro characterization of the anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab, BMS-936558, and in vivo toxicology in non-human primates. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2:846–856. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0040. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources